Figure 6.
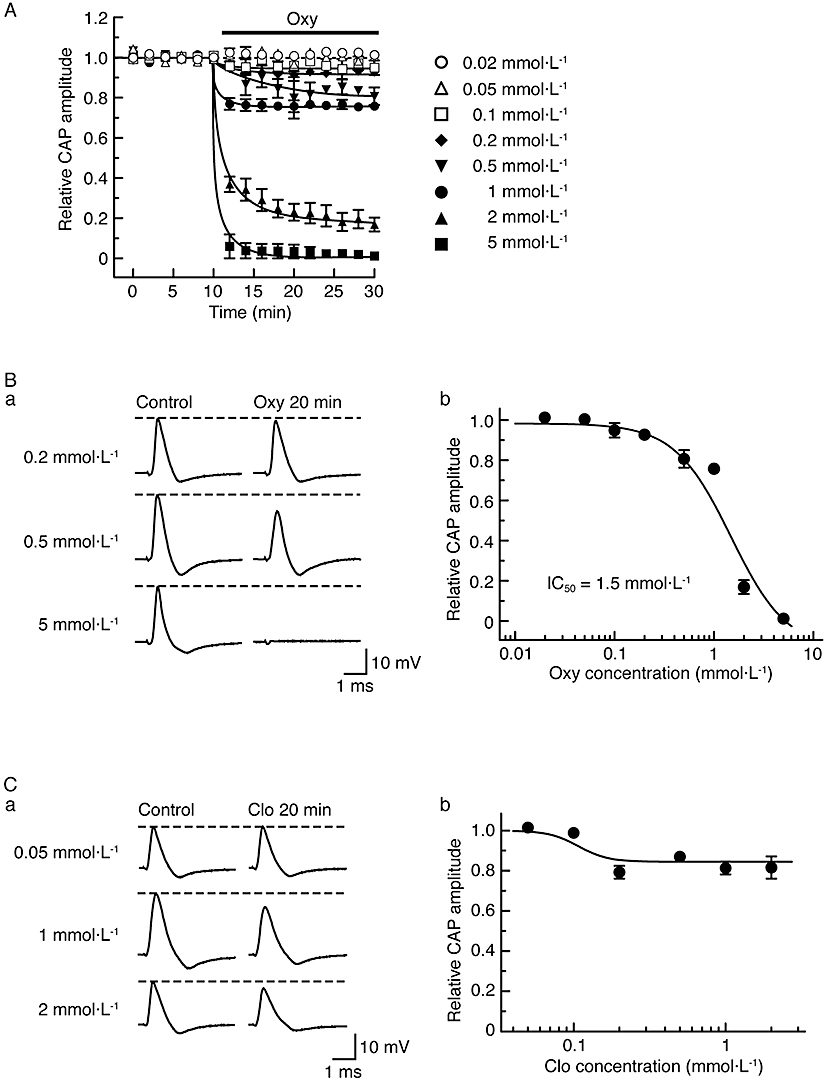
α2-Adrenoceptor agonists, oxymetazoline (Oxy) and clonidine (Clo), reduce compound action potential (CAP) peak amplitudes in a concentration-dependent manner. (A) Comparison in average time course among CAP peak amplitude reductions produced by oxymetazoline at 0.02–5 mmol·L−1, obtained from 25 sciatic nerves. The solid lines were drawn by eye. (B) Concentration dependence for the effect of oxymetazoline on CAPs. (Ba) Recordings of CAPs in the control (left) and after 20 min of exposure to oxymetazoline at 0.2, 0.5 and 5 mmol·L−1 (right); these were obtained from different sciatic nerves. (Bb) The peak amplitude of CAP recorded from sciatic nerve fibres treated with oxymetazoline at various concentrations for 20 min, relative to control, which was plotted against oxymetazoline concentration. Each of the data points was obtained from 3–4 sciatic nerves. The concentration-response curve in (Bb) was drawn according to the Hill equation (IC50 = 1.5 mmol·L−1, nH = 1.5). (C) Concentration dependence for CAP peak amplitude reduction by clonidine. (Ca) Recordings of CAPs in the control (left) and after 20 min of exposure to clonidine at 0.05, 1 and 2 mmol·L−1 (right); these were obtained from different sciatic nerves. (Cb) The peak amplitude of CAP recorded from sciatic nerve fibres treated with clonidine at various concentrations for 20 min, relative to control, was plotted against clonidine concentration. Each of the data points was obtained from 3–5 sciatic nerves.
