Figure 7.
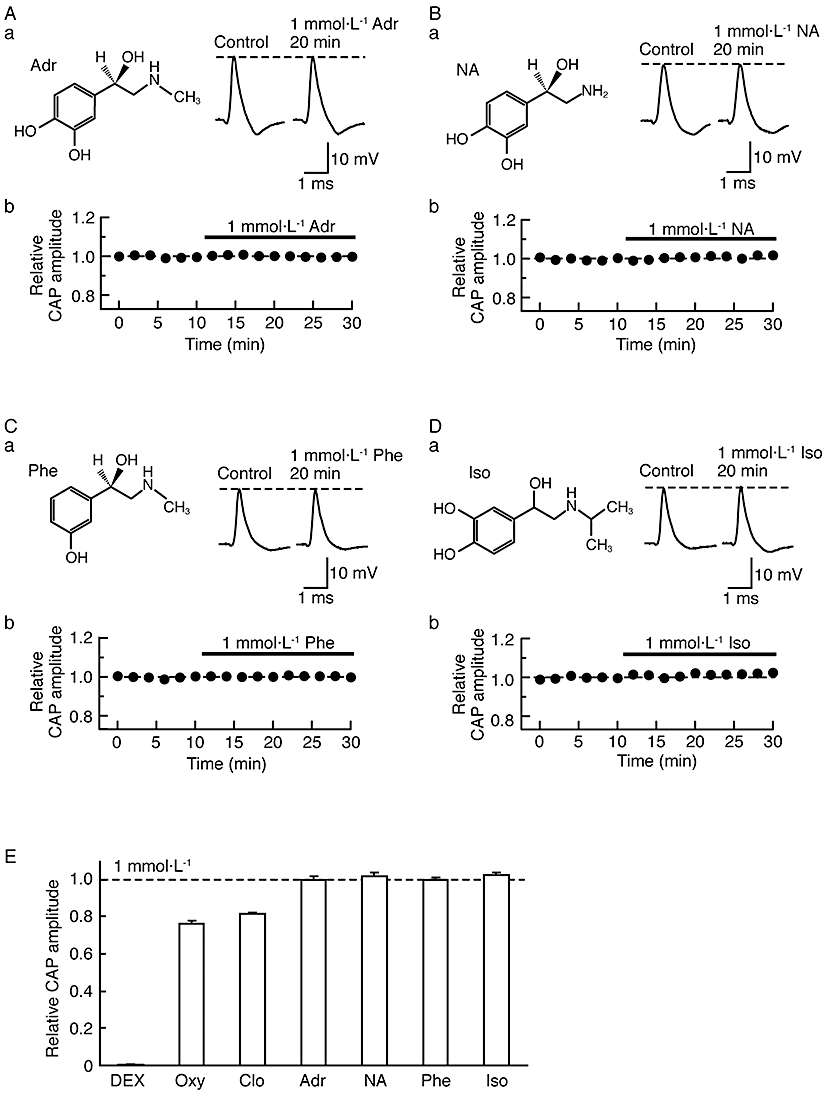
Effects of various adrenoceptor agonists on compound action potentials (CAPs). (Aa, Ba, Ca, Da) Recordings of CAPs in the control (left) and after 20 min of exposure to (±)-adrenaline (Adr; Aa), (±)-noradrenaline (NA; Ba), α1-adrenoceptor agonist (-)-phenylephrine (Phe; Ca) or β-adrenoceptor agonist (-)-isoprenaline (Iso; Da) at 1 mmol·L−1 (right); these were obtained from different sciatic nerves. Insets in (Aa), (Ba), (Ca) and (Da) show the chemical structures of adrenaline, noradrenaline, phenylephrine and isoprenaline, respectively (see Westfall and Westfall, 2006). (Ab, Bb, Cb, Db) Average time courses of changes in CAP peak amplitudes following treatment with adrenaline (Ab; n = 3), noradrenaline (Bb; n = 3), phenylephrine (Cb; n = 3) or isoprenaline (Db; n = 3), relative to that before drug treatment. (E) CAP amplitude (Relative CAP amplitude) after 20 min of exposure to adrenoceptor agonists [dexmedetomidine (DEX), Oxy, Clo, Adr, NA, Phe and Iso; each 1 mmol·L−1], relative to control. The relative CAP amplitudes under the actions of DEX, oxymetazoline and clonidine were taken from Figures 3Bb, 6Bb and Cb, respectively.
