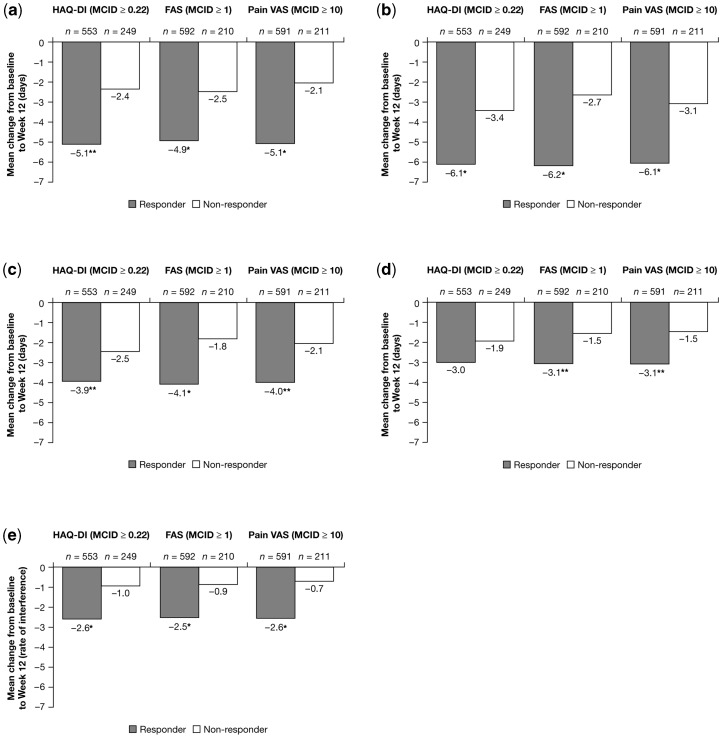
Fig. 2.
Mean changes in household work productivity and daily activities from baseline to Week 12 by responder status (observed data, ITT population, pooled RAPID 1 and 2 CZP 200 mg + 400 mg groups). Response is defined as change from baseline to Week 12 ≥MCID (in absolute value), non-response is defined as mean change from baseline to Week 12 <MCID. Recall period for household work days missed, household work days with productivity reduced by ≥50% (not including household work days missed), leisure days missed and days with hired help is 1 month; range for productivity interference is 0–10, where 0 indicates no interference and 10 indicates complete interference. (a) Reduction in days of household work missed due to arthritis. *P≤0.001 vs non-responders; **P≤0.01 vs non-responders. (b) Decrease in days with household productivity reduced by ≥50% due to RA. *P≤0.001 vs non-responders. (c) Reduction in days lost of family, social or leisure activities due to arthritis. *P≤0.001 vs non-responders; **P≤0.01 vs non-responders. (d) Reduction in days with hired outside help. **P≤0.01 vs non-responders. (e) Reduction in the rate of RA interference with household work productivity. *P≤0.001 vs non-responders; rate of interference 0–10 scale: 0 indicates no interference and 10 indicates complete interference.