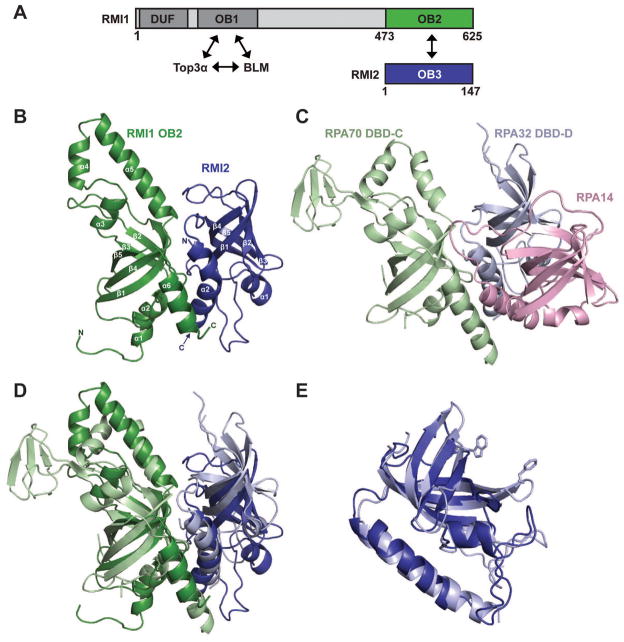
Figure 1. Structural features of the RMI core complex.
(A) Schematic diagram of the domain structures of human RMI1 and RMI2. Interacting OB domains comprising the RMI core complex are shown in green (RMI1 OB2) and blue (RMI2 OB3). Additional RMI1 domains (domain of unknown function, DUF, and an OB domain that interacts with Top3α and BLM (OB1)) are indicated. (B) Ribbon diagram of the crystal structure of the RMI core complex. RMI1 OB2 (green, residues 475-625), and RMI2 (blue, residues 17-147) are rendered using PyMol (Delano, 2002). (C) Ribbon diagram of the crystal structure of the RPA trimerization core (Bochkareva et al., 2002) shown with RPA70 in the same orientation as RMI1 OB2 in (B). RPA70 DBD-C (pale green), RPA32 DBD-D (pale blue), and RPA14 (pink) are shown. (D) Superposition of RMI1 OB2 with RPA70 DBD-C. The color scheme and orientation are presented as in (B) and (C). (E) Superposition of RMI2 with RPA32 DBD-D (Deng et al., 2007). DNA-stacking side chains are shown for RPA32 DBD-D. There are no analogous aromatic residues in RMI2. See also figure S1.