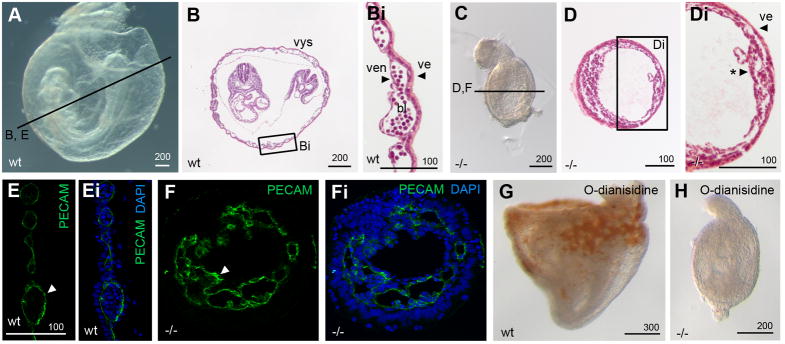
Figure 7. Mesoderm in Pofut2 mutants preferentially differentiates into vascular endothelial cells.
(A–Di) Whole mount and (B and D) transverse hematoxylin and eosin Y stained sections of E 8.5 wildtype (A–Bi) and Pofut2 mutant (C–Di) embryos. (E–Fi) Immunofluorescence staining with PECAM antibody (green indicated by white arrowhead) and DAPI (blue) in E 8.5 control (E–Ei) and RST434 mutant littermates (F–Fi). Approximate plane of sectioning for panels (B, D–G) are indicated by black lines in A and C. Bi and Di represent enlargements of boxed regions in panel B and D. (G, H) O-dianisidine staining of E 8.5 wild type (G) and mutant (H) embryos. Number of mutant embryos represented by panels: C (9), D (7), PECAM (9), O-dianisidine (6). For panels A–D and G and H anterior is left; posterior is right. Proximal is up; distal is down. Abbreviations: bl, primitive erythrocytes; ve, visceral endoderm; ven, vascular endothelial cells; *, condensed mesoderm. Scale bar sizes indicated in μm.