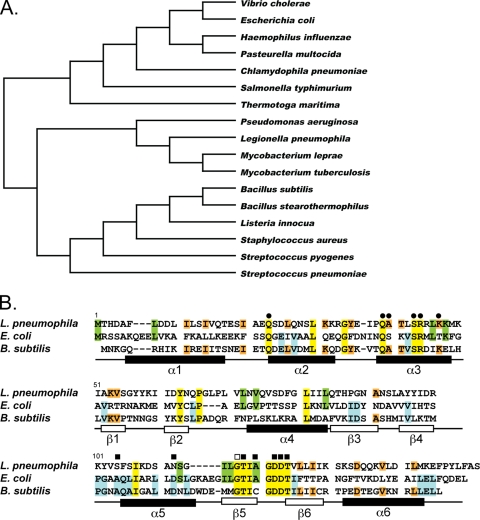
FIG. 1.
Conservation of ArgR. A phylogenetic tree of arginine repressor homologs from diverse bacterial species was produced from a ClustalW alignment (A). GenBank accession numbers for all proteins can be found in Materials and Methods. Shown is the ClustalW alignment of amino acid sequences from E. coli and B. subtilis arginine repressors, ArgR and AhrC, respectively, with the translated sequence from lpg0490 of L. pneumophila (B). Residues conserved among all three bacterial species are highlighted in yellow, those conserved between E. coli and L. pneumophila are in green, those conserved between B. subtilis and L. pneumophila are in orange, and those conserved between E. coli and B. subtilis are in blue (B). Residues required for DNA-binding (•), l-arginine binding (▪), or oligomerization (□) demonstrated by mutational analysis in either E. coli or B. subtilis are indicated above the alignment (B) (8, 41, 76, 82, 83). The general structural features from B. stearothermophilus are shown below the amino acid alignments (B) (62).