FIG. 1.
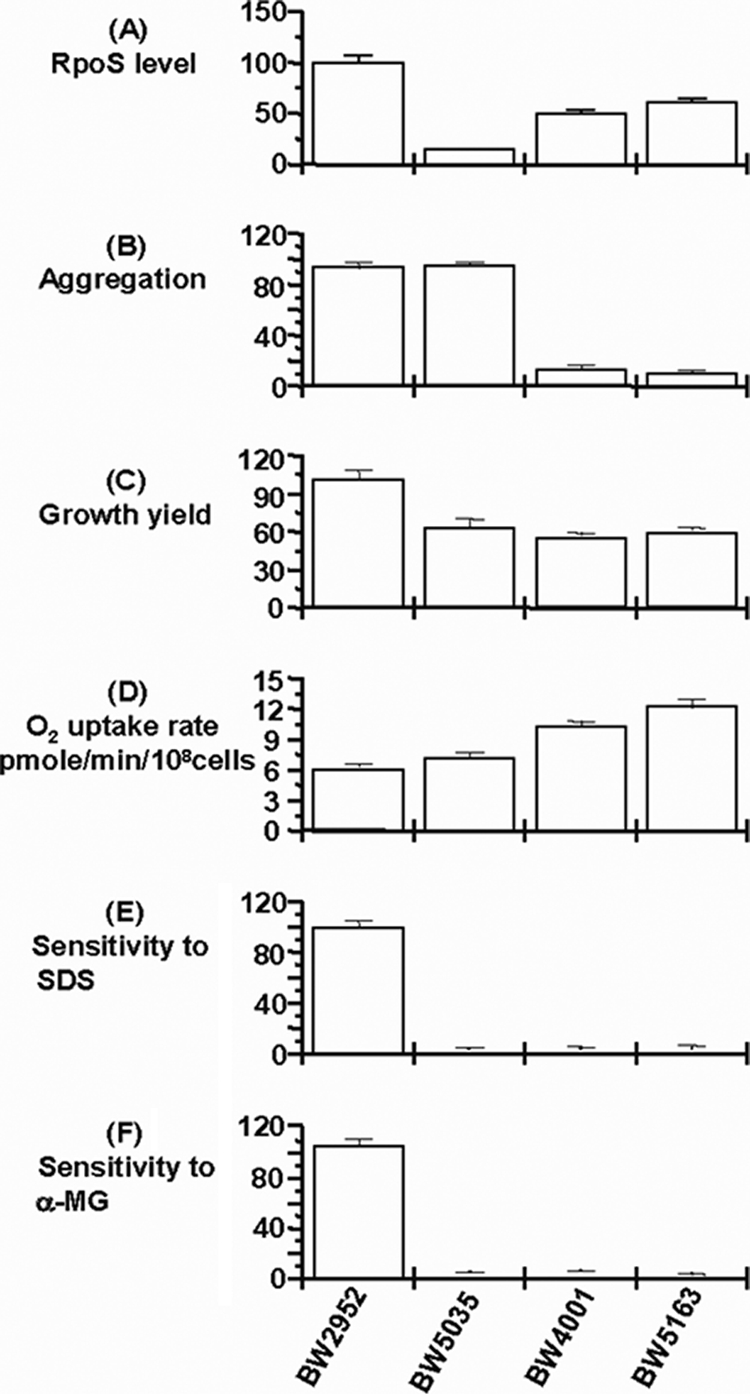
Phenotypic properties of BW4001. The evolved strain BW4001 was derived from the ancestral strain BW2952 (9, 19). BW5035 is derived from BW2952 by insertion of an ampicillin resistance-conferring cassette into the hfq gene by the protocol described previously (34). BW5163 is strain BW2952 in which the BW4001-evolved hfq allele has been transferred in two steps: a purA::tet mutation is first introduced into BW2952 (creating an adenine-auxotrophic strain BW5155) and then the purA-hfq region is introduced into BW5155 using a P1 lysate grown on BW4001 and selecting for PurA+. The transfer of the hfq4001 allele was confirmed by sequencing. (A) The RpoS level was estimated by glycogen staining. Scanning densities relative to that of the ancestor BW2952 are shown. (B) The aggregation of cells was measured based on the decrease in optical density of a standing culture as described in reference 19 and is given relative to that of the ancestor. (C) The growth yield of strains was measured based on the absorbance in L broth after overnight growth to steady state and is shown relative to that of the ancestor. (D) The oxygen uptake rate was measured using an oxygen electrode as described in reference 18. (E) The sensitivity to 2% SDS was measured in patches on L agar plates. Patches were scanned densitometrically, and the cell density relative to that of the ancestor is shown. (F) The sensitivity to 1% methyl α-glucoside was measured in patches on glycerol plates. Patches were scanned densitometrically, and the cell density relative to that of the ancestor is shown.
