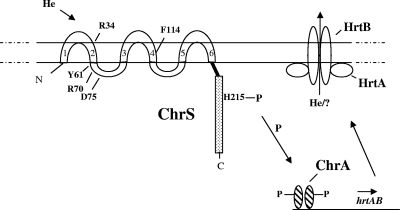
FIG. 6.
Schematic representation of ChrSA regulation of hrtAB and proposed function of HrtAB. In the presence of a heme source, hemin or heme-associated factors are proposed to interact with the membrane-anchored N terminus of ChrS, which results in autophosphorylation at H215 and the subsequent transphosphorylation of ChrA. Phosphorylated ChrA is proposed to bind upstream of the hrtB promoter to activate transcription. The products of hrtAB are predicted to be components of an ABC transporter that may function as an efflux pump to export hemin or factors produced in response to hemin exposure. The locations of amino acids that were identified from mutagenesis studies and are critical for ChrS function are indicated in the ChrS sensor domain. The six transmembrane regions in the N-terminal of ChrS are numbered 1 to 6.