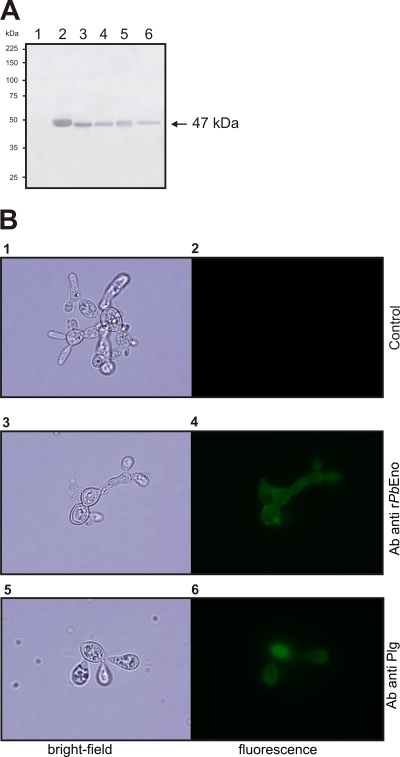
FIG. 2.
Detection of PbEno and plasminogen binding at the cell surface of P. brasiliensis. Experiments were performed in triplicate. (A) Western blot analysis of bovine serum albumin (BSA; lane 1), rPbEno (lane 2), P. brasiliensis crude protein extract (lane 3), cell wall-enriched fraction proteins (lane 4), the soluble cytoplasmic fraction (lane 5), and secreted proteins (lane 6) blotted onto a nylon membrane and detected with rabbit polyclonal anti-recombinant enolase antibodies. The arrow indicates enolase. (B) Paraformaldehyde-fixed, nonpermeabilized cells were incubated with rPbEno antibodies (panels 3 and 4) or treated with human plasminogen followed by incubation with an antibody raised to this protein (panels 5 and 6). Control systems were obtained with anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G (IgG) coupled to alkaline phosphatase antibody only (panels 1 and 2). Bright-field microscopy is shown in left panels. The same cells are shown under the fluorescence mode in the right panels.