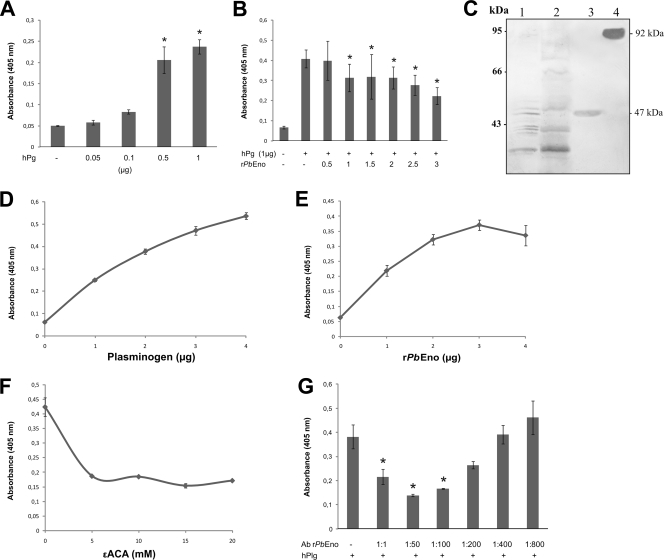
FIG. 3.
Plasminogen binding assays. Microtiter plates were coated with fixed P. brasiliensis yeast cells as detailed in Materials and Methods. (A) Plasminogen (0.05 to 1.0 μg) binds to fixed P. brasiliensis in a concentration-dependent manner. (B) In a competition assay, binding of plasminogen is inhibited by increasing amounts of rPbEno (0.5 to 3.0 μg). (C) Binding of P. brasiliensis proteins to plasminogen. P. brasiliensis crude protein extract (lane 1), cell wall-enriched fraction proteins (lane 2), rPbEno (lane 3), and hPlg (lane 4) were sequentially incubated with plasminogen and a mouse monoclonal anti-human plasminogen antibody. The numbers on the left side are molecular size markers. (D) Plasminogen (1 to 4 μg) binds to rPbEno (1 μg) immobilized on microtiter well plates in a concentration-dependent manner. ELISAs were developed at A405 with antiplasminogen antibody. (E) rPbEno (1 to 4 μg) binds to immobilized plasminogen (1 μg) in a similar fashion. The assay was developed at A405 with antibodies to rPbEno. (F) Effects of different ɛ-ACA concentrations (5 to 20 mM) on plasminogen binding. (G) Plasminogen binding to immobilized rPbEno is specifically inhibited by anti-rPbEno. Microtiter plates were coated by overnight incubation with 1 μg of rPbEno. After blocking, the wells were incubated with decreasing concentrations of rabbit polyclonal rPbEno antibodies. Reactions were developed after incubation with hPlg, the antiplasminogen antibody followed by secondary antibodies. Panels A, B, D, E, F, and G show the averages of three independent experiments performed in triplicates. The error bars indicate the standard deviations from three independent experiments performed in triplicate. *, significantly different from control, at a P value of <0.05.