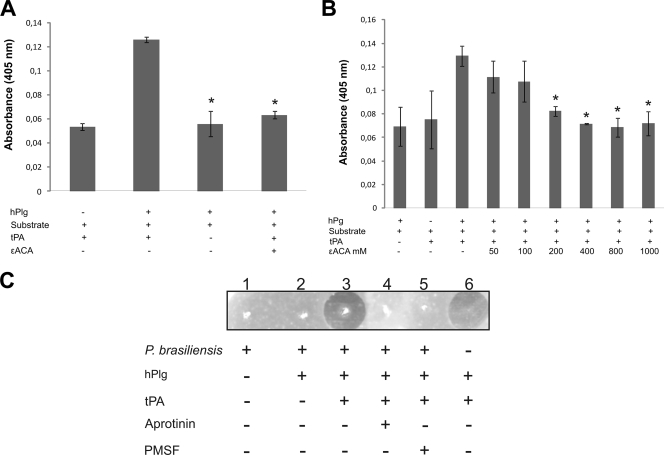
FIG. 4.
Plasminogen activation assays. (A) rPbEno (1 μg) generates plasmin from plasminogen in the presence of tPA and in the absence of ɛ-ACA. (B) P. brasiliensis converts plasminogen into plasmin in the presence of tPA. Various concentrations of ɛ-ACA (50 mM to 1,000 mM) were added to wells containing fixed P. brasiliensis, followed by the addition of plasminogen, and an ELISA was performed as described in Materials and Methods. The error bars indicate the standard deviations from three independent experiments performed in triplicate. *, significantly different from control, at a P value of <0.05. (C) Fibrinolytic activity of plasminogen-bound P. brasiliensis. Lane 1, P. brasiliensis cells in the absence of plasminogen; lane 2, P. brasiliensis cells after binding to plasminogen. Lanes 3, 4, and 5 are similar to lane 2, except that they reflect the presence of tPA, tPA plus aprotinin, and tPA plus PMSF, respectively. Lane 6, controls consisting of plasminogen and tPA.