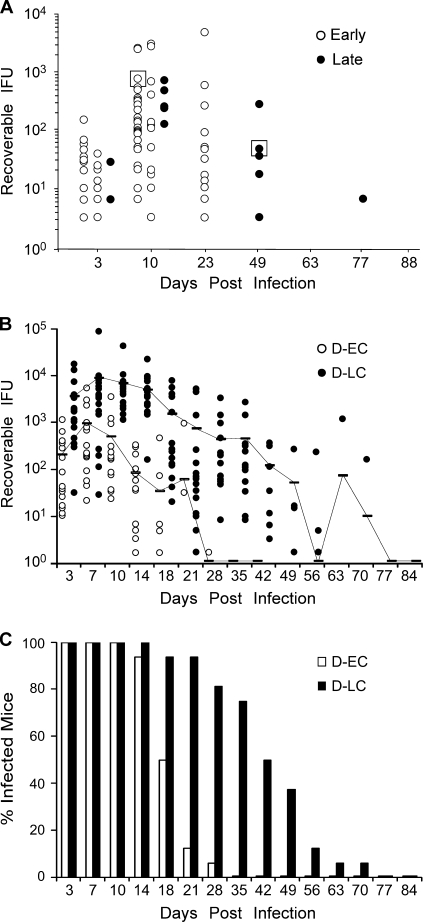
FIG. 1.
In vivo isolation of C. trachomatis infection phenotypes. (A) Fifty-six C3H/HeJ mice were infected with 105 IFU parental strain D/UW-3/CX, and the course of infection was monitored by culture. The results for culture-positive mice are plotted. Infection durations varied from early (10 to 23 days; open circles) to late (49 to 77 days; closed circles). Chlamydiae were isolated from a single early-clearance (D-EC) or late-clearance (D-LC) strain-infected mouse (boxed) and serially passed in McCoy cells (five passages) to obtain sufficient amounts of organisms to rechallenge naïve animals. (B) Sixteen mice were infected with 105 IFU of D-EC or D-LC, and the course of the infection was monitored by culture. Each data point indicates the number of IFU cultured from a single mouse infected with either D-EC (open circle) or D-LC (filled circle). The results for culture-positive mice are plotted. Samples from mice were cultured until inclusion-negative samples were obtained at two successive time points. Contiguous lines indicate the 16-mouse mean IFU values for both groups and include the results for both positive and negative cultures. Mice infected with the individual isolates exhibited distinctly separate infection and clearance kinetics, suggesting that the in vivo-selected strains were clonal. (C) Data for the same groups whose results are shown in panel A plotted as the percentage of infected mice. The percentage of infected mice in the D-LC group was consistently greater in the later culture periods (days 18 to 42).