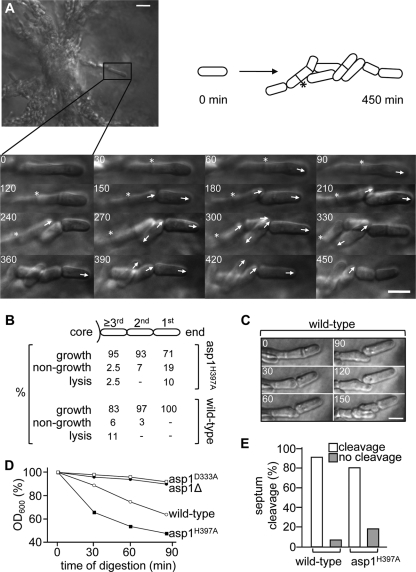
FIG. 4.
Live cell analysis of invasively growing S. pombe cells. (A) Agar blocks containing invasively growing cells were placed in a temperature-controlled microscope chamber. Growth of cells growing at the end of pseudohyphae was monitored for up to 9 h at 30°C. The asp1H397A cell marked with a box was monitored for 7.5 h. The progeny produced by cells growing away from the colony is shown by photomicrographs and depicted diagrammatically. Numbers indicate minutes, arrows the orientation of growth, and the asterisks a septum that did not resolve during the analysis. Bar, 5 μm. (B) Wild-type or asp1H397A cells were monitored as described in the legend to panel A and growth, nongrowth, or lysis of cells at the very end or within pseudohyphae was counted. (C) Example of morphological alterations in invasively growing wild-type cells. Bar, 5 μm. (D) Cells of the indicated genotypes were treated with zymolyase for 90 min, and decrease of the optical density at 600 nm (OD600) was measured to assess cell lysis. (E) Percentage of cleaved or noncleaved septa of wild-type or asp1H397A cells that were monitored as described in the legend to panel A.