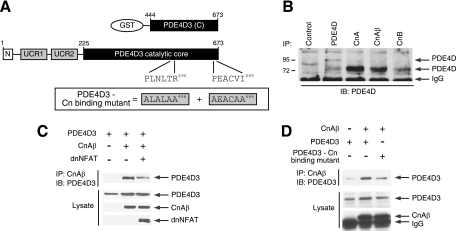
FIG. 5.
Direct interaction between calcineurin and PDE4D. (A) Schematic illustration of PDE4D3 and PDE4D3 GST fusion protein. Functional calcineurin docking motifs (PLNLTR496 and PEACVI666) are indicated. Calcineurin binding-defective PDE4D3 (ALALAA496 and AEACAA666) is also shown. (B) Binding of endogenous PDE4D and calcineurin was determined by coimmunoprecipitation assays. Endogenous PDE4D in COS7 cells was immunoprecipitated (IP) using goat polyclonal PDE4D antibody (sc25097), mouse monoclonal calcineurin A antibody (sc17808), goat polyclonal calcineurin Aβ antibody (sc6124), or goat polyclonal calcineurin B antibody (sc6119). The presence of endogenous PDE4D in calcineurin immunoprecipitates was analyzed by immunoblot (IB) analysis using rabbit polyclonal PDE4D antibody (sc25814). Mouse M2 monoclonal antibody was used as a control. (C) PDE4D3 was coexpressed with CnAβ in COS7 cells. Binding of PDE4D3 and CnAβ was determined by coimmunoprecipitation assays. The presence of PDE4D3 in CnAβ immunoprecipitates and in cell extracts was analyzed by immunoblot analysis. The effect of the PXIXIT-containing calcineurin docking inhibitor dnNFAT is also shown. (D) Wild-type and calcineurin binding-defective PDE4D3 were coexpressed in the presence and absence of CnAβ in COS7 cells. The presence of PDE4D3 in CnAβ immunoprecipitates and in cell extracts was analyzed by immunoblotting.