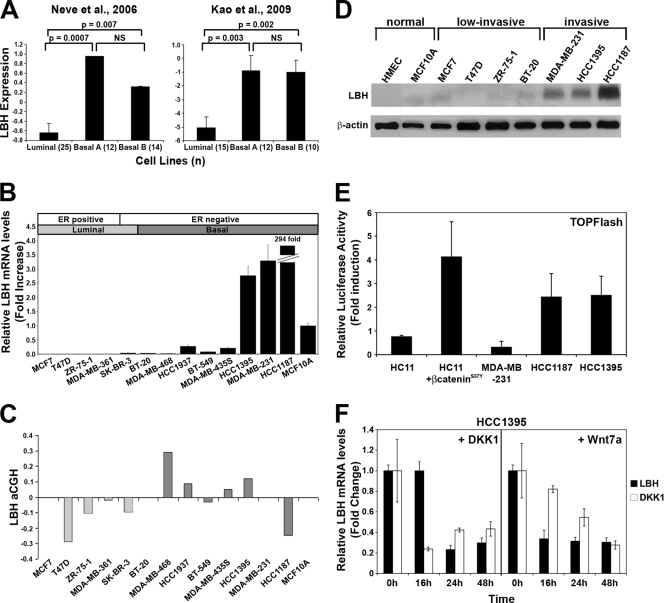
FIG. 7.
Validation of LBH expression and Wnt responsiveness in human breast tumor cell lines. (A) LBH mRNA expression is significantly higher in basal rather than in luminal breast carcinoma cell lines classified according to tumor subtype (36, 49). Values represent the means, and error bars represent the standard errors. (n), number of samples per tumor subtype; NS, not significant. (B) qPCR analysis of relative LBH mRNA expression in a panel of human breast tumor cell lines showing overexpression of LBH in HCC1395, MDA-MB-231, and HCC1187 tumor cells. Cell lines are arranged by tumor subtype (49). All measurements were performed in triplicate, and expression levels were normalized to mRNA levels of GAPDH. (C) Comparative genomic hybridization array (aCGH) analysis of the same breast tumor cell lines as those in panel B. (D) Western blot analysis detecting expression of LBH protein exclusively in invasive ER-negative basal type breast cancer lines but not in two nontransformed (normal) mammary epithelial cell lines or in low-invasive breast tumor cell lines. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (E) TOPFlash reporter assay detects Wnt signaling activity in LBH-expressing HCC1395 and HCC1187 cells but not in MDA-MB-231 cells. HC11 and HC11 transiently transfected with pCDNA3/β-cateninS37Y were used as negative and positive controls, respectively. Values represent the mean ratios of TOPFlash over FOPFlash activity ± standard deviations. (F) Administration of recombinant DKK1 and Wnt7a (100 μg/ml) for the indicated time points strongly inhibits LBH and DKK1 mRNA expression in HCC1395 cells as revealed by qPCR analysis. Values represent means ± standard errors of the means (n = 3).