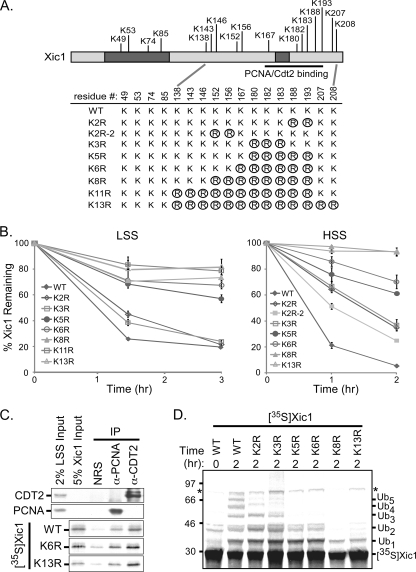
FIG. 6.
Xic1 lysine residues adjacent to the PCNA binding domain are critical for efficient Xic1 turnover. (A) Schematic representation of Xic1, the PCNA and Cdt2 binding regions of Xic1, all the lysine residues of Xic1, and the targeted lysine-to-arginine mutations generated within Xic1. The shaded portions indicate the CDK2-cyclin binding domain (left) and the PCNA binding domain (right). Wild-type Xic1 and seven Xic1 mutants were generated containing lysine (K)-to-arginine (R, circled) mutations at specific residues as indicated. (B) Quantitation of Xic1 degradation assays. The 35S-labeled Xic1 wild type and mutants were incubated in LSS supplemented with Xenopus sperm chromatin or HSS supplemented with ΦX174 single-stranded DNA and analyzed at the time points indicated. The mean percentage of Xic1 remaining from at least three independent experiments is shown, where the 0-h time point was normalized to 100% of Xic1 remaining. SEMs are shown as error bars for each sample. Dependent sample or paired t test analysis between K5R and WT, K6R, K8R, or K13R was performed. K5R versus WT, P values of 0.01 (LSS) and 0.02 (HSS); K5R versus K6R, P value of 0.2 (LSS and HSS); K5R versus K8R, P values of 0.13 (LSS) and 0.04 (HSS); K5R versus K13R, P value of 0.04 (LSS and HSS). (C) PCNA and Cdt2 coimmunoprecipitation assay. Immunoaffinity-purified PCNA (anti-PCNA) and XCdt2 (anti-CDT2) from the egg extract were incubated with 35S-labeled WT Xic1, K6R, and K13R. Normal rabbit serum was used as a negative control for the immunoprecipitations, and samples were immunoblotted with antibody to Cdt2 or PCNA to confirm efficient immunoprecipitation of these proteins. Input samples for the Cdt2 and PCNA immunoblots and for the 35S-labeled Xic1 are shown. (D) Xic1 ubiquitination assay. 35S-labeled WT Xic1 or mutants (K2R, K3R, K5R, K6R, K8R, K13R) were incubated in the HSS supplemented with 3 μg/μl methyl ubiquitin at 0 and 120 min. Monoubiquitinated Xic1 species (Ubn) are shown on the right, and molecular mass markers are shown in kilodaltons on the left. The asterisk indicates a nonspecific in vitro translation product.