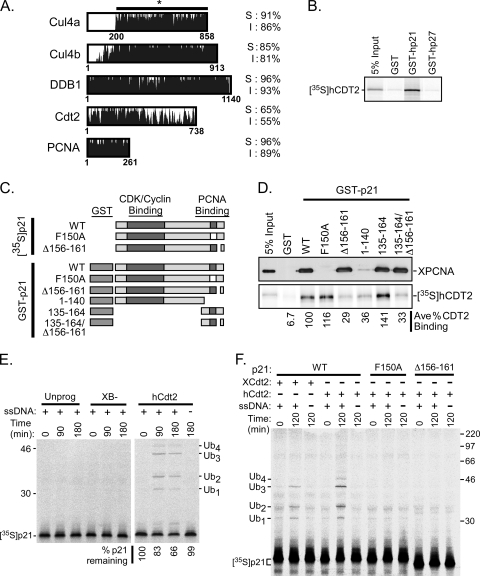
FIG. 7.
p21 is ubiquitinated during the events of DNA polymerase switching/elongation in the Xenopus egg extract. (A) Amino acid sequence similarity between Xenopus and human Cul4a, Cul4b, DDB1, Cdt2, and PCNA. Xenopus residue numbers are indicated at the bottom of the sequence alignments, and the percentages of similarity (S) and identity (I) between the Xenopus and human proteins are shown on the right. Xenopus Cul4a, the MGC115611 protein (gi 71679818), contains 200 additional residues in the N terminus compared to human Cul4a, so only residues 200 to 858 of Xenopus Cul4a were compared in the alignment. (B) GST pulldown assay. GST, GST-p21, or GST-p27 proteins were immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose beads and incubated with 35S-hCDT2. A total of 5% of the input hCdt2 is shown (5% input). (C) Schematic representation of p21 mutants. CDK-cyclin and PCNA binding domains for untagged and GST-tagged p21 mutants are indicated. In the p21 point mutant F150A, phenylalanine is replaced by alanine at residue 150. Mutant Δ156-161 contains a deletion of residues 156 to 161, while other deletion mutants are named by the remaining residues of p21. (D) GST pulldown assay. (Top) GST or GST-p21 wild-type or mutant proteins were bound to glutathione-Sepharose beads, followed by incubation with 10 μl of HSS in NETN buffer. The bead fraction was analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-hPCNA antibody (Santa Cruz), and 0.5 μl HSS was included as an input control (5% input). (Bottom) GST or GST-p21 wild-type or mutant proteins were immobilized onto glutathione-Sepharose beads, followed by incubation with 35S-hCDT2 and analysis by SDS-PAGE and phosphorimaging. The average percentage of hCdt2 bound (ave % CDT2 binding) was calculated using results from 2 independent experiments and was normalized to the level of hCdt2 binding to wild-type p21, which was set at 100%. (E) p21 ubiquitination and degradation assay. 35S-labeled wild-type p21 was incubated in HSS supplemented with 2.5 μl XB− buffer, unprogrammed reticulocyte lysate (unprog; lysate programmed with vector DNA), or in vitro-translated hCdt2 with (+) or without (−) single-stranded DNA (ssDNA). Samples were analyzed at time points between 0 and 180 min as indicated. Ubiquitinated p21 species (Ubn) are shown on the right, and molecular mass markers are shown in kilodaltons on the left. The percentage of p21 remaining at each time point was calculated as a percentage of the amount of p21 at the zero time point, which was normalized to 100%. (F) p21 ubiquitination assay. 35S-labeled wild-type p21 (WT), the p21F150A point mutant (F150A), or the p21Δ156-161 deletion mutant (Δ156-161) was incubated in HSS supplemented with 2.5 μl in vitro-translated Xenopus Cdt2 (XCdt2) or human Cdt2 (hCdt2) as indicated in the presence (+) or absence (−) of single-stranded DNA (ssDNA), followed by analysis at 0 and 120 min. Ubiquitinated p21 species (Ubn) are shown on the left, and molecular mass markers are shown in kilodaltons on the right.