FIG. 8.
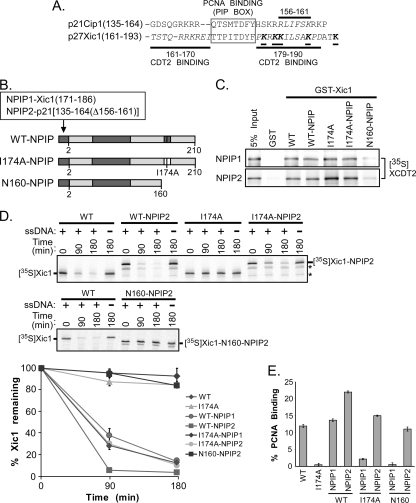
Xic1 turnover does not require the tandem arrangement of PCNA and Cdt2 binding domains. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment of p21 (p21Cip1) and Xic1 (p27Xic1). Cdt2 binding regions indicated by italicized amino acid residues and bold lines, the PCNA binding element (PIP box) indicated by gray box, and critical lysine residues of Xic1 indicated by underlining, italicizing, and boldfacing of amino acid residues. (B) Schematic representation of mutant Xic1 proteins. CDK2-cyclin and wild-type PCNA binding domains are indicated by dark gray shading, while the I174A PCNA binding mutant is indicated by a white box. Xic1 residue numbers are indicated below each schematic. The NPIP1 and NPIP2 domains are fused to the N terminus of wild-type Xic1 (WT-NPIP), Xic1-I174A (I174A-NPIP), or amino acids 1 to 160 of Xic1 (N160-NPIP) as indicated and includes Xic1 amino acids 171 to 186 (TTPITDYFPKRKKILS) for NPIP1 and p21 residues 135 to 164 with an internal deletion of residues 156 to 161 for NPIP2. The NPIP2 domain serves solely as a PCNA binding domain and does not retain the ability to efficiently bind Cdt2. (C) GST pulldown assay. GST or GST-Xic1 wild-type and mutant proteins (top, NPIP1; bottom, NPIP2) were immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose beads and incubated with 35S-labeled Xenopus Cdt2 (35S-XCDT2). The 35S-XCdt2 input control (5% input) is shown in lane 1. (D) Xic1 degradation assay. (Top and middle) 35S-labeled Xic1 wild-type (WT) and mutant proteins (WT-NPIP2, I174A, I174A-NPIP2, and N160-NPIP2) as indicated were incubated in HSS with (+) or without (−) single-stranded DNA for the indicated times, followed by SDS-PAGE and phosphorimager analysis. Asterisks indicate internal initiation translation products. (Bottom) Quantitation of Xic1 degradation. The mean percentage of Xic1 remaining from two (WT, WT-NPIP1, I174A-NPIP1, and N160-NPIP1) or three (WT-NPIP2, I174A, I174A-NPIP2, and N160-NPIP2) independent experiments as described above is shown, where the 0-h time point was normalized to 100% of Xic1 remaining for each sample. SEMs are shown as error bars. (E) Quantitation of Xic1 binding to PCNA. GST or GST-PCNA proteins were immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose beads and incubated with 35S-labeled Xic1 wild-type (WT) or mutant proteins (I174A, WT-NPIP1, I174A-NPIP1, N160-NPIP1, WT-NPIP2, I174A-NPIP2, and N160-NPIP2). The average percentage of Xic1 bound by GST-PCNA (% PCNA binding) is shown, where values for WT Xic1 and I174A are averages of results from 4 independent experiments, and the values of the NPIP mutants (WT-NPIP1, I174A-NPIP1, N160-NPIP1, WT-NPIP2, I174A-NPIP2, and N160-NPIP2) are averages of results from 2 independent experiments. SEMs are shown as error bars.