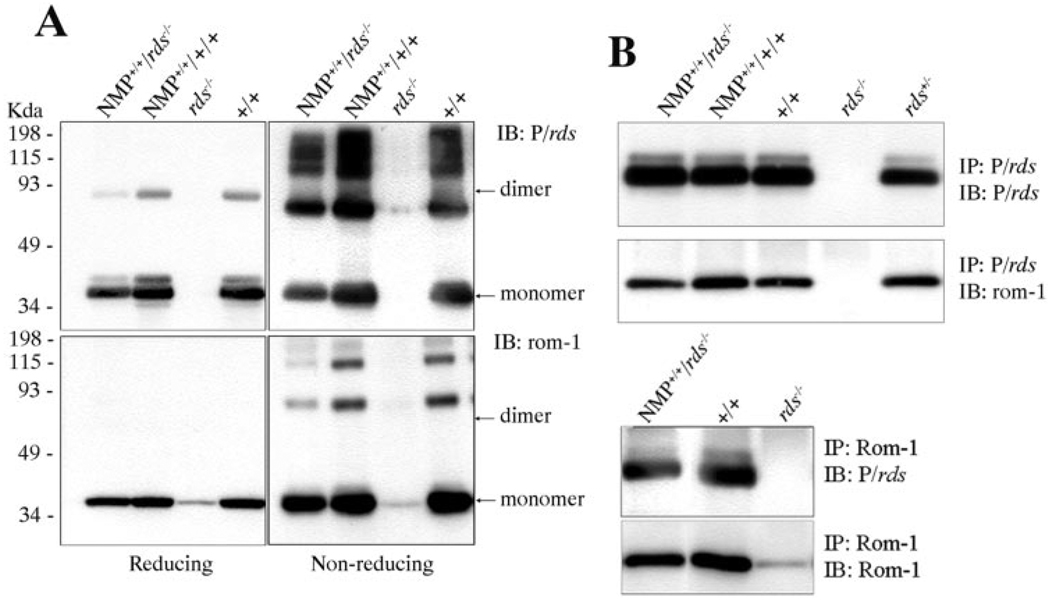
FIGURE 2.
Biochemical properties of the NMP protein. (A) Blot analysis of NMP protein under reducing and nonreducing conditions. Under reducing conditions, the major band of P/rds (top left) migrated as a monomer, with lesser amounts corresponding to the dimer also detected, whereas Rom-1 migrated as a monomer (lower left) in retinal samples from both NMP and wild-type mice. Under nonreducing conditions, dimer and higher-order oligomers of P/rds (top right) and Rom-1 (bottom right) were predominant. (B) Reciprocal Co-IP using anti-P/rds (top) and anti-Rom-1 (bottom) antibodies showing a comparable pattern of association between P/rds and Rom-1 in both NMP and wild-type retinas, indicating that the NMP protein is able to interact with Rom-1. Retinal samples from rds−/− mice were included as a negative control.