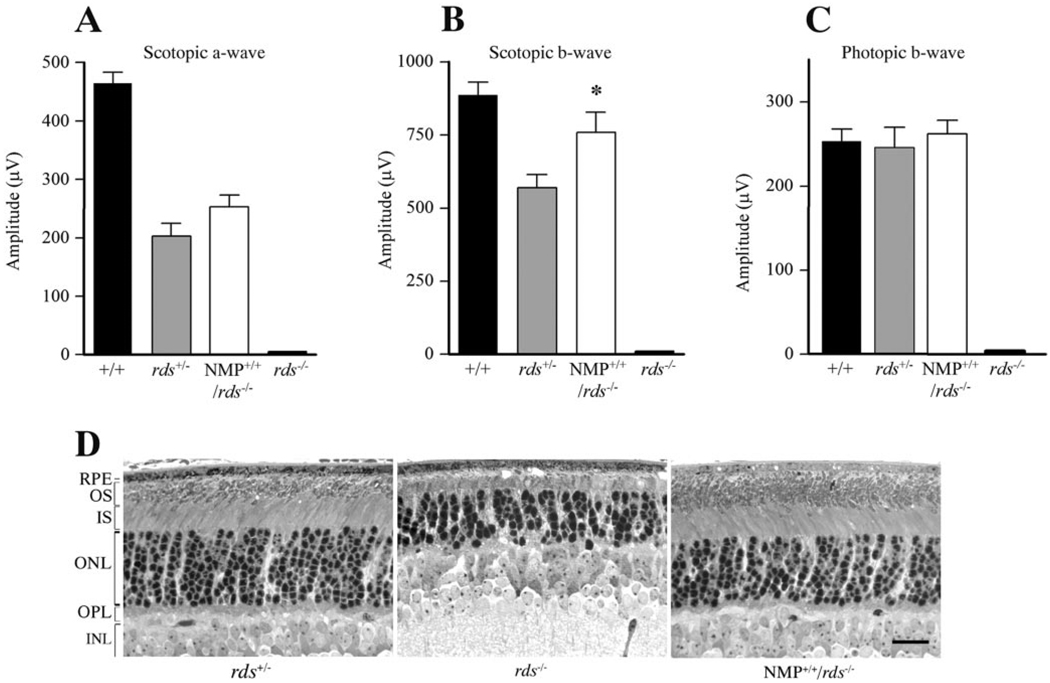
FIGURE 3.
NMP-mediated functional and structural rescue of the rds−/− retina. (A, B) Scotopic ERG amplitudes show an NMP-mediated restoration of rod photoreceptor function when compared with responses from rds−/−. Note that the expression levels of P/rds in rds+/− (50% of wild type) and NMP+/+/rds−/− (60% of wild type) correlate well with the increase in scotopic ERG amplitudes. (C) Photopic ERG amplitudes demonstrate that one allele of P/rds is sufficient to support normal cone photoreceptor function, as revealed by photopic ERG responses from rds+/− and NMP+/+/rds−/− retinas. No rod or cone ERG signal was detected in rds−/− mice. ERG results are an average of 12 to 16 eyes for each genotype at 1 month of age. (D) Light microscopy of retinas taken at 30 days of age from rds−/− (middle), NMP+/+/rds−/− (right), and rds+/− mice (left). Note the lack of OS formation in rds−/−, whereas a notable improvement in inner and OS structure was seen in NMP+/+/rd−/− retinas. Outer nuclear layer count corresponds to 9 to 10, 6 to 7, and 9 to 10 rows in rds+/−, rds−/−, and NMP+/+/rds−/− retinas, respectively. Scale bar, 20 µm.