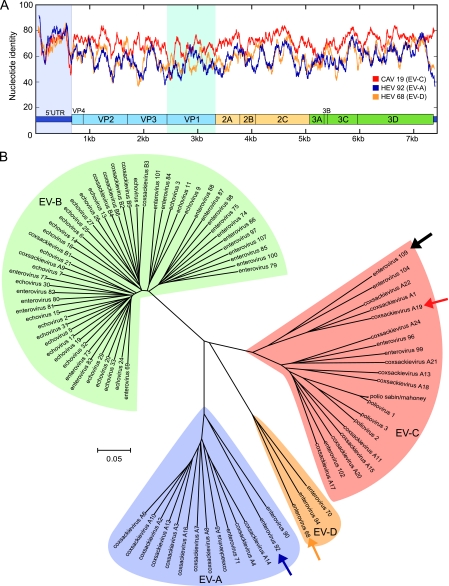
FIG. 3.
Relationships between known enteroviruses and EV109 based on full-length genome analysis. (A) Full-genome similarity plot depicting scanning pairwise identity using a 100-nt sliding window evaluated at each nucleotide. The EV109 sequence is compared with a close HEV-C relative, coxsackievirus A19 (CAV19) and more distant HEV-A (EV92) and HEV-D (EV68) serotypes. The conserved enteroviral domains are depicted to scale. The 5′ UTR and VP1 regions are highlighted. (B) Phylogenetic tree constructed from complete enterovirus genomes. The EV109 genome sequenced in this study is depicted with a solid black arrow, coxsackievirus A19 is identified by a red arrow, enterovirus 92 is identified by a purple arrow, and enterovirus 68 is identified by a yellow arrow. ClustalW and MEGA were used for alignments and tree construction, respectively, using the neighbor-joining method and 500 bootstrap replicates.