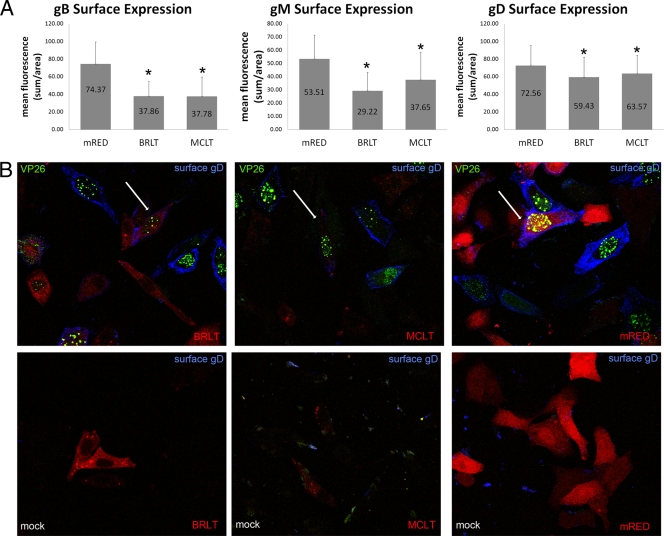
FIG. 6.
(A) Quantification of gB, gM, and gD surface expression in the presence of dominant negative myoVa. HEp-2 cells were transfected with mRED-DN-myoVa-BRLT, mRED-DN-myoVa-MCLT, or mRED control vector. Transfected cells were infected with HSV-1 K26-GFP (MOI = 10 PFU per cell) or mock infected at 26 h posttransfection. At 15.5 hpi the cells were washed with PBS, fixed in 3% PFA for 15 min, and blocked in 10% human serum. The fixed, unpermeabilized cells were immunostained with gD, gB, or gM antibody. K26-infected cells expressing the mRED control, mRED-DN-myoVa BRLT, or mRED-DN-myoVa MCLT were identified at random by intrinsic red and GFP fluorescence, and the amount of glycoprotein-specific fluorescence was quantified using a Zeiss Imager.M1 Axio fluorescent microscope and IP Lab v3.65a software. At least 50 infected cells expressing each construct were analyzed. Mean fluorescence is the sum of measured fluorescence divided by the area. The mRED-DN-myoVa BRLT- and MCLT-expressing cells were determined by Student's t test (P < 0.05) to have less surface expression of gB, gM, and gD compared to that of mRED control cells. (B) Expression of DN-myoVa decreases glycoprotein immunoreactivity on the surfaces of HSV-infected HEp-2 cells. Example of K26-infected cells transfected with DN-myoVa or the mRED control demonstrating decreased immunoreactivity with gD antibody in DN-myoVa-expressing cells. White arrows indicate cells of interest. Similar results were seen for gM and gB staining (data not shown). Green, HSV-1; blue, gD; red, DN-myoVa or mRED control.