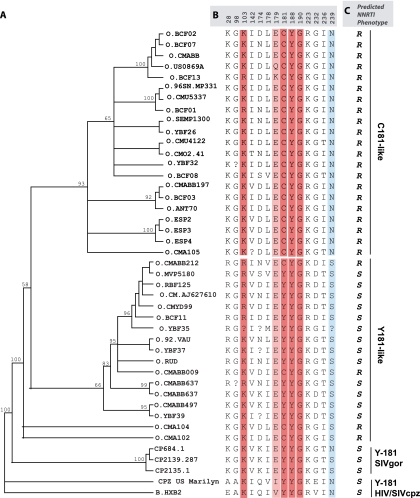
FIG. 2.
Phylogenetic analyses of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group O evolution in the reverse transcriptase gene. (A) Neighbor joining phylogenetic analysis was performed with the first 750 nucleotides from 38 HIV-1 group O and 3 SIVgor group O-like sequences obtained from the Los Alamos HIV database (see Materials and Methods and the legend to Fig. 1). (B) Signature amino acid residues were identified using VESPA and are grouped as C181-like or Y181-like sequences. CMO2.41, the clone used in this study, is in the C181-like cluster. The majority of group O sequences are C181-like, and the minority bears Y181 and cluster more closely with HIV-1 group M (HXB2). The amino acid positions are indicated at the top of the sequence. Question marks represent positions with no clear amino acid, as outlined in the Los Alamos database. Amino acids known to confer high- and low-level resistance to NNRTIs are indicated in dark red and light red, respectively. Completely conserved positions (>99%) are shown in sky blue. (C) Predicted NNRTI phenotypes are indicated as R (resistant) or S (susceptible).