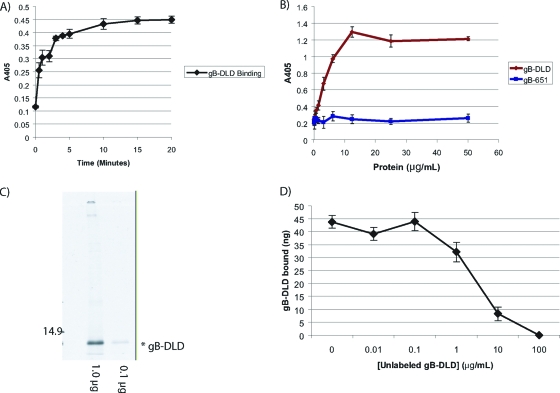
FIG. 2.
Binding properties of the gB disintegrin-like domain. (A) gB-DLD binds permissive human fibroblasts with rapid kinetics. NHDF cells were incubated with a constant concentration (10 μg/ml) of gB-DLD at 4°C in 96-well plates after blocking with 1 mg/ml BSA. Cells were incubated for the indicated times, washed, fixed, and probed for the gB-DLD His6 tag by cell enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). (B) gB-DLD binds permissive human fibroblasts in a dose-dependent and saturable manner. Increasing concentrations of gB-DLD or gB-651 were added to NHDF cells for 60 min at 4°C, and cells were washed, fixed, and assayed for bound protein by cell ELISA. (C) Audioradiograph of 35S-labeled gB-DLD. E. coli cells were grown in the absence of sulfate prior to recombinant protein induction and the addition of 35S. A sample of the prep was separated by SDS-PAGE and exposed to film overnight. A prominent band at approximately 12 kDa corresponds to the predicted mass of gB-DLD. The specific activity of this preparation was 56,207 cpm/μg. (D) Homologous competition. A constant concentration of radiolabeled gB-DLD (1 μg/ml) was added to human fibroblasts in the presence of increasing concentrations of cold gB-DLD. Nonspecific binding was determined by the addition of a 100-fold molar excess and was determined to be 19%.