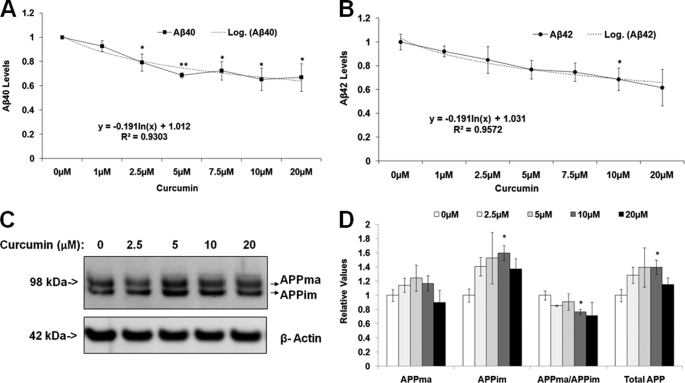
FIGURE 1.
Curcumin significantly decreases Aβ levels and the ratio of APPma:APPim in mouse primary cortical neurons in a dose-dependent manner. A and B, curcumin significantly decreases both Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels. Mouse primary cortical neurons (E18) were treated with different concentrations of curcumin and harvested after 24 h. Conditioned medium was used in ELISA analysis to detect the Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels, which were normalized to cell numbers. C and D, the curcumin treatment altered APP levels and decreased the ratio of APPma:APPim. In the Western blotting analysis, cell lysates were probed with the APP8717 antibody to reveal APP. β-Actin was used as the loading control. C, a representative gel showing full-length APP and β-actin. D, densitometry of C (n = 3 for each treatment group). Mean ± S.E. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.