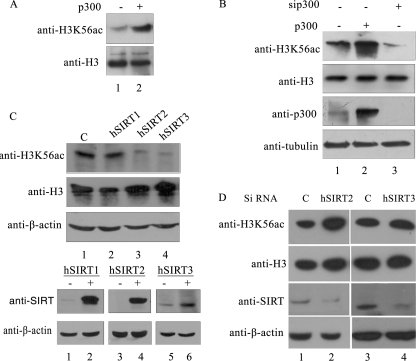
FIGURE 3.
Enzymes involved in the acetylation and deacetylation of H3K56 in human system. A, p300-mediated in vitro acetylation of histones extracted from HEK 293T cells. In vitro acetylation reaction was performed in the presence (lane 1) or absence (lane 2) of recombinant p300 as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The upper panel depicts immunoblot analysis using anti-H3K56ac antibodies, whereas the level of total H3 is shown in the lower panel. B, p300 acetylates H3K56 in vivo. p300 was overexpressed (lane 2) and silenced (lane 3) separately in HEK 293T cells as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The histones were isolated and immunoblotted for monitoring H3K56ac and H3 levels (upper two panels). Expression of p300 and tubulin was monitored by immunoblot analysis of the same samples. C and D, hSIRT2 and hSIRT3 deacetylate H3K56 in vivo. Sirtuins involved in the deacetylation of H3K56ac were tested by monitoring the reduction in the level of H3K56 acetylation upon overexpression of hSIRT1, hSIRT2, and hSIRT3 (C) and siRNA-mediated knockdown of hSIRT2 and hSIRT3 (D) by transient transfection in HEK 293T cells as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Immunoblotting anti-H3 and anti-β-actin was used as a loading control. Expression of the three sirtuins was confirmed using immunoblotting of lysates from control (−) and transfected (+) cells using anti-SIRT antibody (upper panel). Immunoblot with anti-β-actin (lower panel) was used as a loading control.