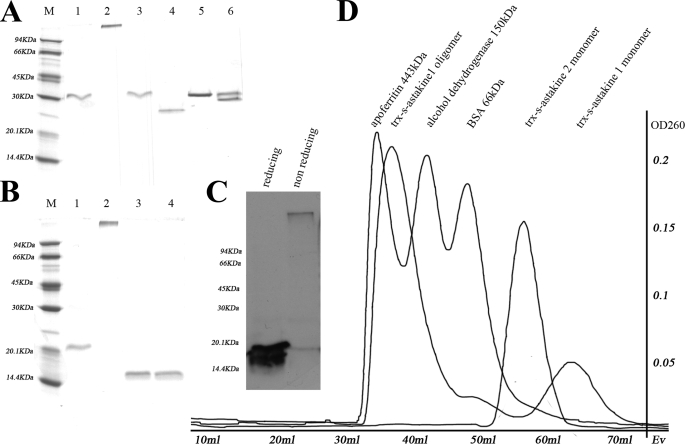
FIGURE 5.
Astakine 1 and astakine 2 move differently in SDS-PAGE. A, recombinant astakine 1 shows an oligomer and a monomer, but recombinant astakine 2 only runs as a monomer. Lane 1, r-astakine 1 (Trx-S tag-astakine 1) in reducing conditions (molecular mass is about 30 kDa); lane 2, r-askakine1 (Trx-S tag-astakine 1) in non-reducing conditions (molecular mass is about 370 kDa, which was measured by Gel filtration); lane 3, monomer of r-astakine 1 (Trx-S tag-astakine 1) in reducing conditions (purified by gel filtration); lane 4, monomer of r-astakine 1 (Trx-S tag-astakine 1) in non-reducing conditions (purified by gel filtration); lane 5, r-astakine 2 (Trx-S tag-astakine 2) in reducing conditions; lane 6, r-astakine 2 (Trx-S tag-astakine 2) in non-reducing conditions. B, oligomer formation of r-astakine 1 is independent of the fusion tag. The oligomer form of r-astakine 1 was treated with the protease thrombin to remove the fusion tag Trx. Lane 1, r-astakine 1 without Trx tag in reducing conditions; lane 2, r-astakine 1 without Trx tag in non-reducing conditions; lane 3, free Trx in reducing conditions; lane 4, free Trx in non-reducing conditions. C, r-astakine 1 expressed in the insect cell-baculovirus expression system similarly forms oligomers. Lysates of Sf9 cells infected with recombinant baculovirus containing the ORF of astakine 1 were used for Western blot using astakine 1 antibody. D, in order to separate the oligomer and monomer form of recombinant fusion astakine 1, HiPrep 16/60 Sephacryl S-200 HR column (GE Healthcare) gel filtration was performed. Apoferritin (443 kDa), alcohol dehydrogenase (150 kDa), and BSA (66 kDa) were used as standard proteins to calibrate the column.