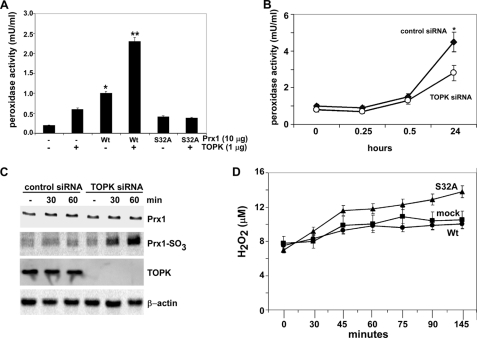
FIGURE 4.
TOPK increases the peroxidase activity of Prx1 and suppresses H2O2 accumulation. A, in vitro peroxidase activity was determined as described under “Materials and Methods” using active TOPK and FPLC purified His-Prx1-Wt (Wt) or His-Prx1-S32A (S32A) fusion proteins. Peroxidase activities of nonphosphorylated Wt and S32A were used as controls. To convert the spectrophotometric data (A570) to peroxidase activity (mU/ml), a peroxidase standard curve was prepared according to the manufacturer's instructions. B, peroxidase activity was determined as for (A), but using RPMI7951 cells (2 × 104) transfected with control siRNA or TOPK siRNA. Samples were harvested at different times following UVB (4 kJ/m2) treatment. Data are shown as means ± S.D. of three samples from two independent experiments. The asterisk (*) indicates a significantly increased (p < 0.001) activity induced by UVB in control siRNA cells compared with untreated or UVB-treated TOPK siRNA cells. C, oxidation of Prx1 to Prx1-SO3 was assessed by Western blotting using anti-Prx1-SO3 (recognizes oxidized Cys-52 in Prx1) after UVB (4 kJ/m2) in RPMI7951 cells transfected with control siRNA or TOPK siRNA. Total TOPK, Prx1, or β-actin protein levels were used as internal controls to confirm TOPK deficiency and equal protein loading. D, effect of TOPK on H2O2 accumulation was measured as for (A) in mock, Prx1 Wt or Prx1 mutant (S32A) stably transfected cells. To convert the spectrophotometric data (A570) to reflect the levels of H2O2 (μm), an H2O2 standard curve was prepared according to the manufacturer's instructions.