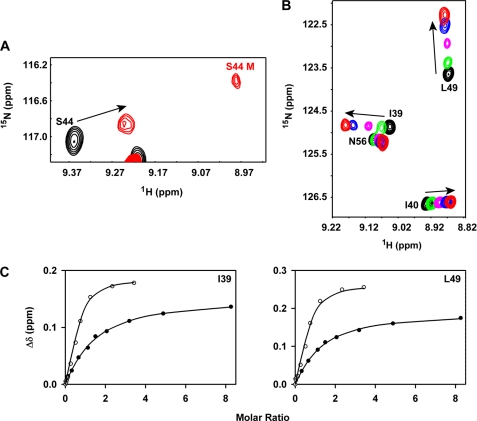
FIGURE 7.
Binding of CC-CXCL8 to CXCR1 N-domain. Panel A, binding induced dissociation of CC-CXCL8 dimer. A section of the 15N-1H HSQC spectra showing binding-induced chemical shift changes in the CC-CXCL8 dimer, and the appearance of bound monomer (labeled in red). Panel B, section of the 15N-1H HSQC spectra showing binding-induced chemical shift perturbations of the CC-CXCL8(1–66) monomer. Unbound peaks are in black and the final bound peaks are in red. Panel C, left and right, binding affinity measurements. Binding-induced chemical shift changes are shown for residues Ile-39 and Leu-49 of CC-CXCL8(1–66) (●) and CXCL8(1–66) (○). Average Kd calculated from a subset of CC-CXCL8(1–66) residues is ∼5-fold lower compared with CXCL8(1–66) monomer (63 ± 6 versus 12 μm).