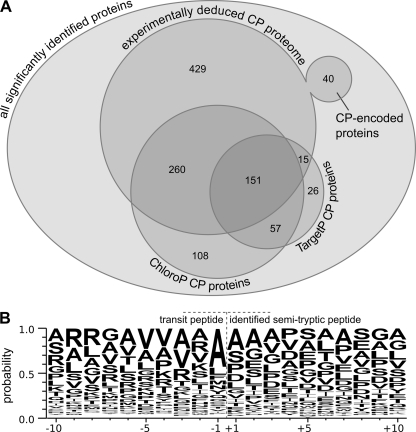
Fig. 5.
Analyses of organelle targeting prediction and transit peptide cleavage specificity using chloroplast-localized proteins. A, from a total of 2315 significantly identified proteins (each of which was identified with at least two distinct peptides or at least one GPF-confirmed peptide at an estimated peptide FPR of 1%), 895 proteins could be localized to the chloroplast (CP). 40 of these proteins are chloroplast-encoded, and the remaining 855 proteins are encoded in the nucleus. The majority of the proteins that were localized to the chloroplast by the localization prediction tools ChloroP and TargetP overlap with the experimentally deduced chloroplast proteome. B, the WebLogo of the identified semitryptic peptides shows an increased probability for alanine at the C terminus of the chloroplast transit peptide as well as the trend that the charge of the 10 amino acids before the cleavage site of the transit peptide is overall positive, whereas the charge of the 10 amino acids after the cleavage site is overall negative. A total of 111 significantly identified semitryptic transit peptides were used along with the amino acid residues surrounding each of the putative transit peptide cleavage sites to generate the WebLogo.