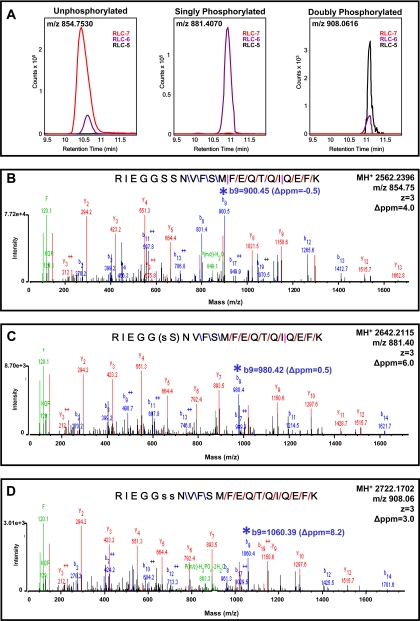
Fig. 5.
MS/MS spectra showing identification of phosphospecies in murine RLC. A, left panel, extracted ion chromatogram of unphosphorylated RLC peptide 9–30 (m/z 854.7530) showing the majority in fraction RLC-7 with minor carryover in RLC-6. Middle panel, extracted ion chromatogram of singly phosphorylated RLC peptide 9–30 (m/z 881.4070) showing the presence of this peptide exclusively in RLC-6. Right panel, extracted ion chromatogram of doubly phosphorylated RLC peptide 9–30 (m/z 908.0616) of RLC showing the majority of this peptide in fraction RLC-5 with minor carryover in RLC-6. B, MS/MS spectra (SPI of 96%; peptide score of 20.8) of unphosphorylated RLC peptide m/z 854.7530 (precursor mass error of 5.8 ppm) with peptide bond cleavage type denoted as follows: blue, b ion; red, y ion; and pink, both b and y ion formation. C, MS/MS spectra (SPI of 91%; peptide score of 20.8) of singly phosphorylated RLC peptide m/z 881.4070 (precursor mass error of 4.2 ppm). s, phosphorylated serine. D, MS/MS spectra (SPI of 96%; peptide score of 19.2) of doubly phosphorylated RLC peptide m/z 908.0616 (precursor mass error of 3.0 ppm). Note the mass shifts and mass accuracy of b9 fragments (*) going from B to D, illustrating a 79.966 shift in each as an additional HPO3 is added to the peptide.