Fig. 5.
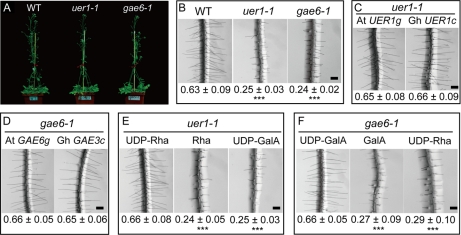
Arabidopsis uer1-1 and gae6-1 mutants were genetically or chemically complemented by expressing a specific cotton cDNA or by supplementing the respective nucleotide sugars in growth medium. A, phenotypes of wild-type Col, uer1-1, and gae6-1 plants at the time of flowering. B, close-up views taken from the fully elongated root hair zone of 10-day-old Arabidopsis seedlings (mean ± S.E. in mm). C, wild-type root hairs were produced on T2 transgenic Arabidopsis seedlings expressing either At UER1g (left) or Gh UER1c (right). D, wild-type root hairs were produced on T2 transgenic Arabidopsis seedlings expressing either At GAE6g (left) or Gh GAE3c (right). E, 5 μm exogenous UDP-Rha (left), but not free Rha (middle) or UDP-GalA (right), chemically complemented the root hair phenotype of uer1-1. F, 5 μm exogenous UDP-GalA (left), but not free GalA (middle) or UDP-Rha (right), chemically complemented the root hair phenotype of gae6-1. Scale bars in B–F, 200 μm. ***, significant at p < 0.001 compared with the wild type.