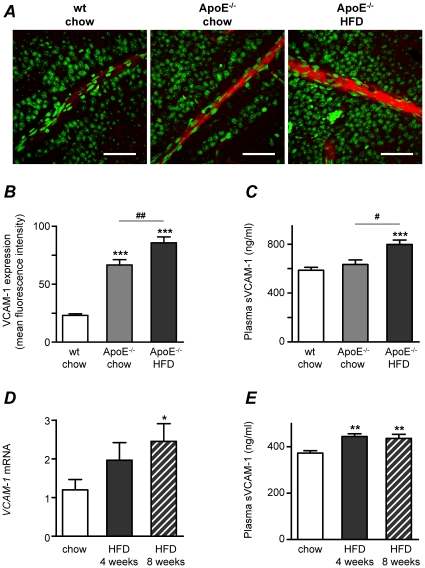
Figure 5. High fat diet (HFD) increases VCAM-1 expression in retinal vessels.
(A) Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy images showing VCAM-1 expression (red) and nuclei stained by SYTOX (green) in retinal whole-mounts from wt mice fed normal chow diet and from ApoE−/− mice fed normal chow or 4 weeks of HFD. Bars = 50 µm. Measurements were performed when mice were 17 weeks of age. (B) Summarized data from experiments as in A, showing increased mean fluorescence intensity of VCAM-1 in ApoE−/− (light gray bar) when compared to wt controls (white bar; ***p<0.001) and further increased VCAM-1 expression in response to HFD (dark gray bar; ## p<0.01). (C) Mean sVCAM-1 concentrations in plasma from the same mice used in A and B. ***p<0.001 vs. wt chow and # p<0.05 for differences between ApoE−/− groups (chow vs. HFD). (D) Expression of VCAM-1 mRNA was studied by real time RT-PCR in normolipidemic FVBN mice. Expression was enhanced by 4 or 8 weeks of HFD (plain and patterned gray bars, respectively) when compared to mice fed regular chow diet (white bars). The effects were significant after 8 weeks (*p<0.05). Values are normalized to the expression of cyclophilin B and GAPDH. (E) Mean sVCAM-1 concentrations in plasma from the same mice used in D. **p<0.01 vs. wt chow.