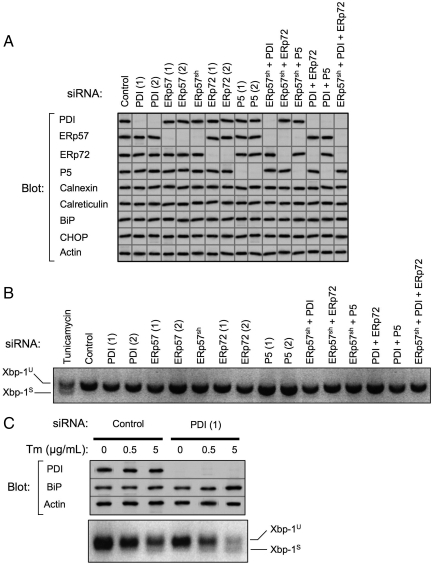
Figure 1.
Efficacy of PDI family member knockdown and assessment of UPR. (A) PDI family members were depleted from HepG2 cells by RNAi over a period of 6 d. Indicated single or multiple knockdowns were carried out transiently using two independent targeting siRNAs, designated (1) and (2), or in some instances using cells constitutively expressing shRNAmir targeting ERp57 (ERp57sh). Equivalent amounts of cell lysates were immunoblotted for PDI family members, ER chaperones, CHOP, and actin. Images shown are a composite from various experiments, all of which included actin as a loading control. Exposures were adjusted to an equivalent density of the actin control. Data are representative of a minimum of five replicate knockdowns. (B) After the indicated knockdowns or overnight treatment with 5 μg/ml tunicamycin, total RNA was isolated from HepG2 cells and analyzed for Xbp-1 splicing by reverse-transcription PCR. Xbp-1U, unspliced Xbp-1 product; Xbp-1S, spliced Xbp-1 product. (C) HepG2 cells were subjected to PDI knockdown for 10 d. On day 9, cells were treated overnight with the indicated concentrations of tunicamycin (Tm). The following day, cell lysates were immunoblotted to detect PDI, BiP, and actin. Lanes shown were assembled from a single gel. Total RNA was also isolated and analyzed for Xbp-1 splicing.