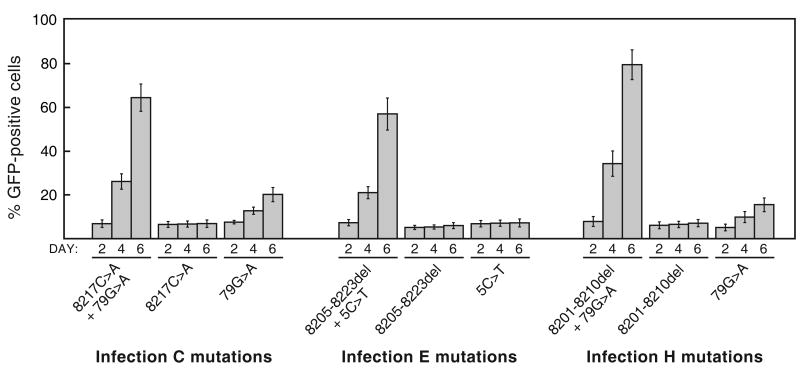
Figure 4.
Evaluation of the importance of each of the LTR mutations from infections C, E and H for viral replication. For each of these three GZAP-GFP mutants, two variants were constructed, each possessing one of the two mutations in isolation. Infections with these variants or the original mutants were carried out using equal doses of virus, and viral spread was assessed by flow cytometry at the indicated days post-infection. Values shown are the average obtained from triplicate infections and error bars indicate standard deviations.