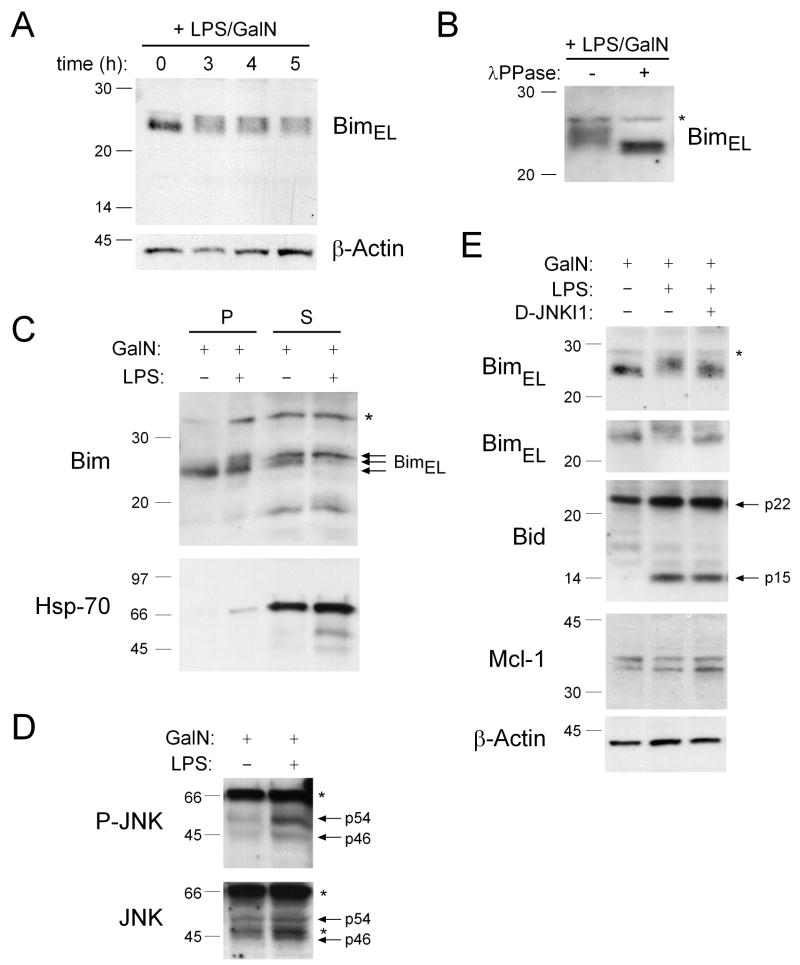
Figure 5. Bim Is Phosphorylated by JNK Kinase in the Livers of Mice Injected with LPS plus GalN.
(A) Mice (wt) were injected with LPS (100 ng) plus GalN (20 mg) and sacrificed at the time points indicated. Levels and post-translational modifications of Bim were investigated in liver-derived total protein extracts by Western blotting. Probing with an antibody to β-actin was used as a loading control. (B) Mice (wt) were injected with LPS (100 ng) plus GalN (20 mg) and sacrificed after 3 h. Total protein extracts were prepared from the liver in the absence of phosphatase inhibitors and left untreated or treated in vitro with λ-phosphatase prior to analyzing Bim modifications by Western blotting. (C) Mice were treated with GalN (20 mg) alone (controls) or with LPS (100 ng) plus GalN (20 mg) and livers harvested after 4 h. Protein extracts were prepared and then subjected to subcellular fractionation into the dynein enriched pellet fraction (P), containing BimEL/L sequestered to microtubules, and a soluble fraction (S) containing free cytosolic Bim. Fractions were analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies to Bim or HSP70 (control for the purity of the fractions). (D) Liver extracts from wt mice treated with 100 ng LPS plus 20 mg GalN for 4 h were probed by Western blotting with an antibody specific for phosphorylated (activated) JNK and the membrane re-probed with an antibody to total JNK (loading control). (E) Wt mice that had either been left untreated or pre-treated for 30 min with the JNK inhibitory peptide D-JNKI1 (20 mg/kg, i.p.) were treated for 4 h with either 20 mg GalN or with 100 ng LPS plus 20 mg GalN. Total liver extracts were probed by Western blotting with antibodies to Bim (two blots from independent experiments shown), Bid, Mcl-1 and β-actin (loading control). Asterix indicate non-specific bands.