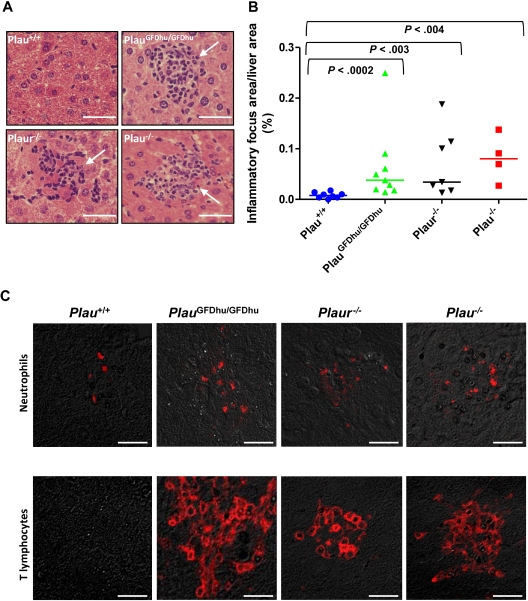
Figure 4.
Chronic inflammation caused by abrogation of uPA-uPAR interaction. (A) Histologic appearance of the livers of 1-year-old Plau+/+ (top left panel), PlauGFDhu/GFDhu (top right panel), Plaur−/− (bottom left panel), and Plau−/− (bottom right panel) mice. Focal leukocyte infiltrates (examples with arrows) are increased in mice with abrogated uPA-uPAR interaction, loss of uPAR, or loss of uPA. Size bars, 50 μm. (B) Enumeration of inflammatory foci in the livers of Plau+/+ (left), PlauGFDhu/GFDhu (second left), Plaur−/− (second right), and Plau−/− (right) mice. Symbols represent individual mice. Horizontal bars show average values. P values were determined by the Mann-Whitney U test, 2-tailed. (C) Examples of immunostaining for neutrophils (myeloperoxidase, top panels) and T lymphocytes (CD3, bottom panels) within inflammatory foci from Plau+/+ (left panels), PlauGFDhu/GFDhu (second panels from left), Plaur−/− (second panels from right), and Plau−/− (right panels) showing prominent infiltration of neutrophils and T lymphocytes into tissues from mice with abrogated uPA-uPAR interaction, but not into mice with unchallenged uPA-uPAR interaction. Size bars, 20 μm.