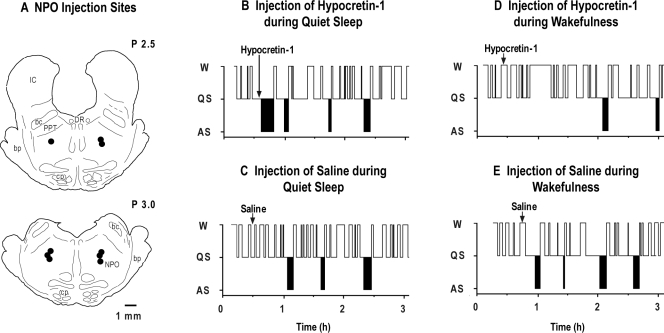
Figure 1.
Schematic presentation of the sites of hypocretin-1 injection in the pons of 5 cats (A). All injection sites, which are indicated by filled circles, are mapped onto coronal brainstem sections at levels P 2.5 and P 3.0. Hypnograms of the effects of (B) the injection of hypocretin-1 during quiet sleep (QS), (C) the injection of saline during QS, (D) the injection of hypocretin-1 during wakefulness (W), and (E) the injection of saline during W from a representative cat. The injection of hypocretin-1 (vertical arrow in B), which was carried out during QS, immediately induced an episode of active sleep (AS). In contrast, the injection of hypocretin-1 during W (vertical arrow in D) induced long-duration episodes of W and blocked the subsequent occurrence of AS for more than 1 hour. bc refers to the brachium conjunctivum; bp, brachium pontis; cp, cerebral peduncle; DR, dorsal raphe nucleus; IC, inferior colliculus; PPT, pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus.