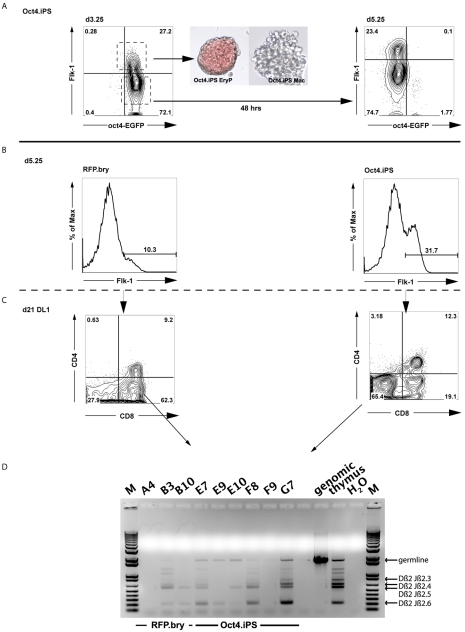
Fig. 7.
Generation and characterization of Flk1pos populations from iPSCs. (A) Oct4-EGFP iPSCs were differentiated in the presence of activin A, BMP4 and VEGF. Flk1pos and Flk1neg cells isolated at d3.25. Flk1pos cells were reaggregated for 24 hours and their hematopoietic potential was tested in a colony-forming assay. A primitive erythroid (EryP) and a macrophage (Mac) colony are shown, generated from the d3.25 Flk1pos population (40× magnification). Flk1neg cells were reaggregated for 48 hours and analyzed by flow cytometry at d5.25 for the emergence of a secondary Flk1pos population. (B) Flow cytometric analyses demonstrating the presence of an Flk1pos population in d5.25 aggregates generated from Oct4-EGFP iPSCs and tdRFP/T-EGFP (RFP.bry) cells. Both cell types were differentiated in the presence of activin A, BMP4 and VEGF. After dissociation at d3.25, the cells were reaggregated without cell sorting and cultured for an additional 48 hours, at which time they were sorted based on the expression of Flk1. (C) Flow cytometric profile demonstrating the generation of CD4+ CD8+ lymphocytes from the d5.25 Flk1pos ESC- and iPSC-derived progenitors following culture on OP9-Dl1 cells for 3 weeks. (D) PCR analyses showing T cell receptor gene rearrangements in the developing T cell populations from either the ESC progenitors (B3, B10) or the iPSC progenitors (E7, E9, E10, F8 and G7). M, 1 kb DNA ladder.