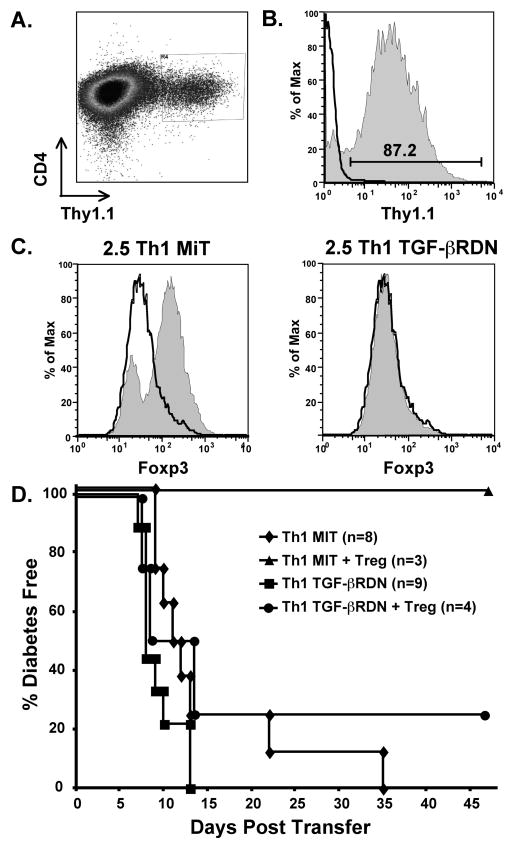
Figure 6. Th1 effectors expressing a non-functional TGF-βRII are not suppressed in vivo by TGF-β-induced Tregs.
2.5 TCR-Tg Th1 T cells were transduced with the empty MiT vector or MiT-TGF-βRDN. A. Transduced cells were isolated by sorting for expression of Thy1.1, shown here on Th1 cells after MiT-TGF-βRDN transduction. B. After sorting, cells were expanded for three days with IL-2 before adoptive transfer. Thy1.1 expression, shown here on MiT-TGF-βRDN-transduced cells, remained high after expansion. The histogram outline represents isotype control staining and the shaded histogram represents Thy1.1 specific staining. C. MiT and MiT-TGF-βRDN-transduced cells were activated in the presence of TGF-β under Foxp3-inducing conditions. The histogram outlines and the shaded histograms represent Foxp3 expression on cells that were activated in the absence or presence of TGF-β, respectively. Foxp3 expression increased on MiT-transduced cells but not MiT-TGF-βRDN-transduced cells. D. 2.5 TCR-Tg Th1 cells (1 × 106) transduced with empty MiT vector or MiT-TGF-βRDN were transferred into adult NOD.scid mice in the absence or presence of 6.9 TCR-Tg TGF-β-induced Tregs (2 × 106). TGF-β-induced Tregs effectively suppressed diabetes induction by Th1 cells containing the MiT vector (p = 0.02), but did not suppress diabetes induction by Th1 cells containing the MiT-TGF-βRDN vector (p = 0.69). Data are combined from four experiments.