Figure 1. Distribution of fatty acid binding proteins (FABPs) in tissues important for long chain fatty acid (LCFA) metabolism.
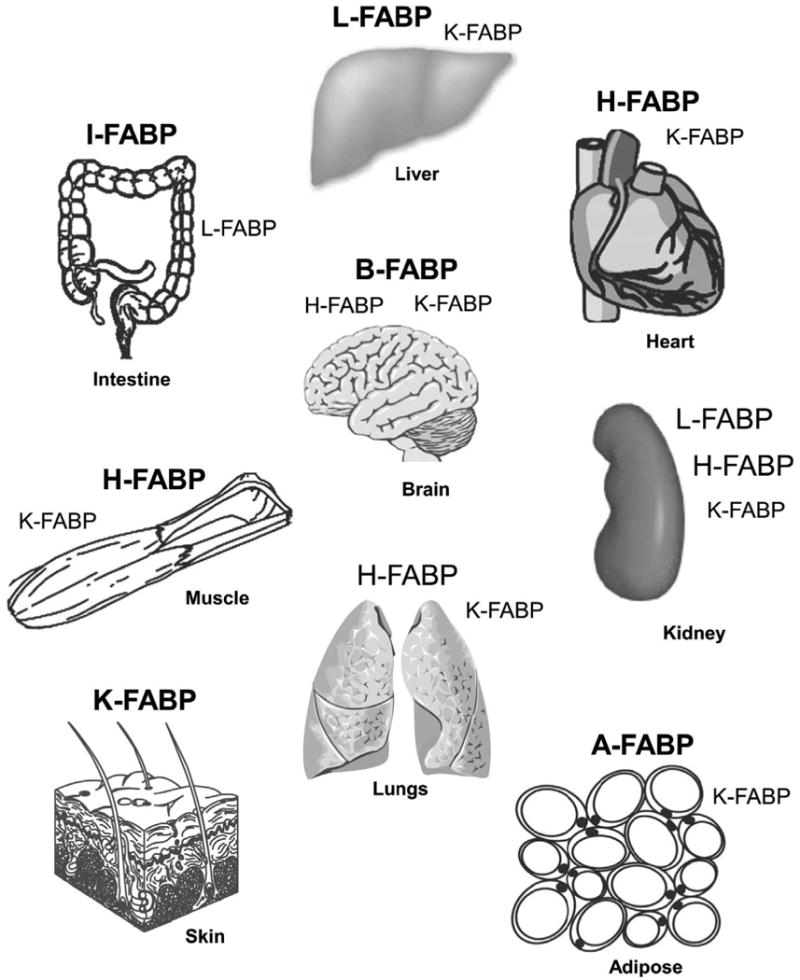
FABPs present in tissues at highest concentration are shown in large bold letters. FABPS present at lower concentration are shown in large unbold letters. Low expression is shown with small bold letters. The nomenclature of the long chain fatty acid binding protein family has been described [21]: L-FABP, liver type fatty acid binding protein (Fabp1 gene); I-FABP, intestinal type fatty acid binding protein (Fabp2 gene); H-FABP, heart type fatty acid binding protein (Fabp3 gene); A-FABP, adipocyte type fatty acid binding protein (Fabp4 gene); K-FABP, keratinocyte type fatty acid binding protein (also called epidermal fatty acid binding protein, E-FABP, Fabp5 gene); B-FABP, brain type fatty acid binding protein (Fabp7 gene). Additional members of the FABP family (not shown) that bind other types of ligands include: M-FABP, myelin (peripheral) type fatty acid binding protein (Fabp8 gene); T-FABP, testis type fatty acid binding protein; ILBP, ileal bile acid binding protein (Fabp6 gene); CRBP I and II, cellular retinol binding proteins I and II; and CRABP I and II, cellular retinoic acid binding proteins I and II.
