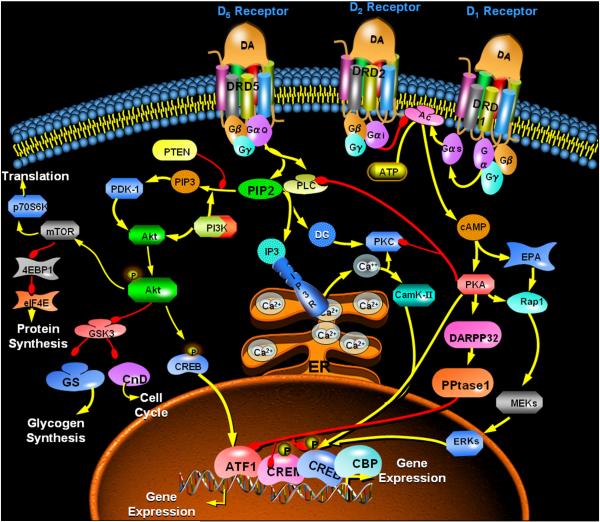
Figure 3.
Schematic of dopamine-sensitive signaling via adenylyl cyclase (AC), phospholipase C (PLC), and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) systems. This simplified view of the signaling pathways shows key downstream mediators and the various opportunities for interaction or integration among the pathways. Note the inhibitory effect of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) on the activity of PLC, an action that provides a mechanism for crosstalk between the AC system and the PI/PLC systems. Besides hampering inositol trisphosphate (IP3)- mediated intracellular calcium mobilization (which would inhibit DARPP32 Thr34 phosphorylation via calmodulin/protein phosphatase 2B), it may also be possible that inhibition of PIP2 (phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate) utilization via PLC could shunt the phospholipid to the PI3K pathway. Red arrows depict inhibition, while yellow arrows depict stimulation. Abbreviations: DA, dopamine; DRD1, Dopamine receptor D1 subtype; DRD2, Dopamine receptor D2 subtype; DRD5, Dopamine receptor D5 subtype; cAMP, cyclic AMP; PKA, protein kinase A; EPAC, Exchange protein activated by cyclic AMP; PPtase1, protein phosphatase 1, MEKs/ERKs, mitogen-activated kinases; ATF1/CREM/CREB/CDP, illustrative transcription-regulatory factors; CamK-II, calcium-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II; DG, diacylglycerol; IP3R, inositol trisphosphate receptor; Ca2+, calcium ions within and exiting the endoplasmic storage; PIP3, phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; PDK-1, phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1; Akt, protein kinase B; GSK3, glycogen synthase kinase-3; CcnD, cyclin D; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; 4EBP1/eIF4E/p70S6K, downstream mediators to protein synthesis.