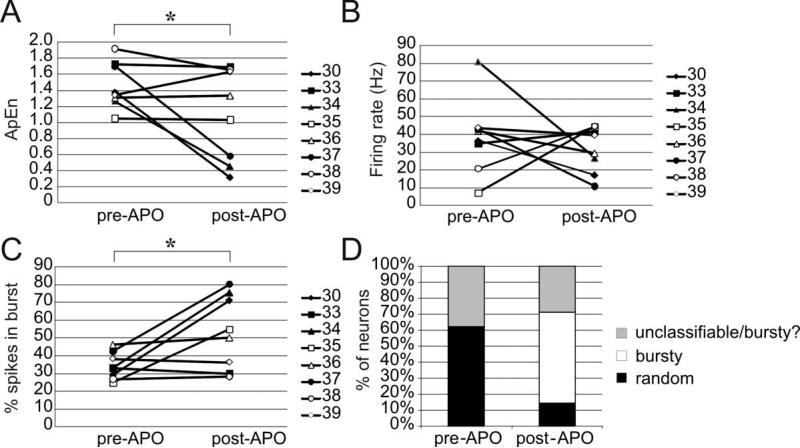
Figure 1.
Changes in firing rates and patterns prior to and following administration of apomorphine. Following apomorphine administration, the ApEn (A) decreased significantly (one-tailed paired t-test, p= 0.046) while the percentage of spikes in bursts (C)increased significantly two-tailed paired t-test, p=0.036. The firing rate (B) did not change significantly in this sample of neurons. As expected due to the increased percentage of spikes in bursts, the prevalence of bursty neurons (using the classification of Kaneoke and Vitek (1996)) increased following apomorphine.