Fig. 2.
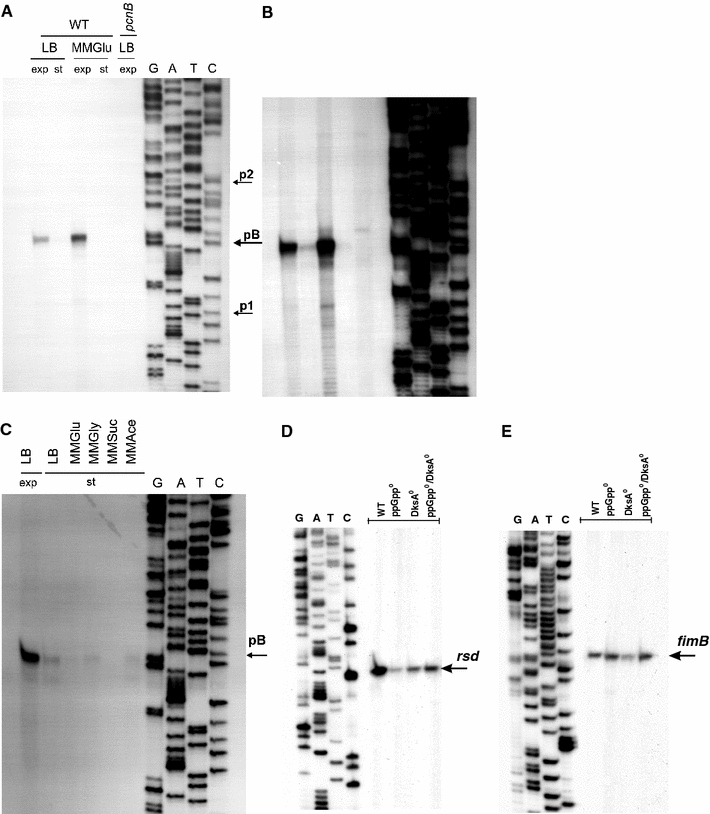
Transcription from the pcnB (a–c), rsd (d) and fimB (e) promoter regions under various growth conditions of bacterial cultures. In experiments shown in a and b, wild-type (WT) E. coli or the pcnB (ΔpcnB::kan) mutant was grown in LB or MMGlu medium, to exponential (exp) or stationary (st) phase of growth at 37°C. Primer extension experiments were performed with primer Pr11 as described in “Materials and methods”, and the products of the reactions were separated during polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, with the products of the sequencing reaction (performed using the same primer) run at the same gel (lanes G, A, T and C). The position of the products of primer extension reactions, corresponding to transcripts originating from the pB promoter, is shown in a. Positions previously reported as p1 and p2 transcription start sites are also marked by arrows. Apart from results of the experiment performed using the standard procedure (shown in a), results of a significantly longer exposition of the same gel during autoradiography are demonstrated (b) to show products corresponding to activities of other promoters. Analogous experiments, but with E. coli cells cultured at the exponential phase in LB medium (LB exp) and at the stationary phase (st) in various media (LB, MMGlu, MMGly, MMSuc, MMAce) are shown in c. In control experiments, levels of the rsd (d) and fimB (e) transcripts in E. coli wt cells (WT), and ppGpp0 (relA spoT double mutant), DksA0 (dksA::kan mutant) and ppGpp0 DksA0 (relA spoT dksA triple mutant) derivatives cultured at the stationary phase (d) or the exponential phase (e) in LB medium. Primer extension experiments were performed with Rsd.rev and FimB.rev primers, and the products of the reactions were separated during polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, with the products of the sequencing reaction (performed using the same primer) run at the same gel (lanes G, A, T and C)
