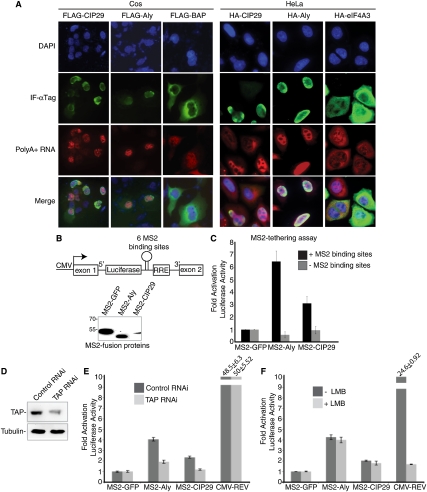
Figure 3.
Evidence that CIP29 functions in mRNA export. (A) IF and FISH for polyA+ RNA in cells transfected with CMV constructs encoding Flag- or HA-tagged CIP29, Aly, BAP, or eIF4A3 in Cos or HeLa cells as indicated. DAPI staining was used to identify the nucleus. Bar, 10 μm. The Cos cells were treated with actinomycin D for 2 h prior to FISH to reduce the nascent RNA levels. Note that the cytoplasmic signals are dampened in the control and nontransfected cells when images are captured at the same exposure as shown for all of the data except Flag-BAP. This dampening occurs because the microscope automatically adjusts the image using the strong signal detected in the nuclei in cells with an export block. For the Flag-BAP FISH data, we showed an overexposure relative to that for Flag-CIP29 and Flag-Aly in order to detect the cytoplasmic signals. (B) Schematic of MS2/RRE reporter construct. The intron contains six MS2-binding sites and one RRE, and encodes luciferase. Westerns of the MS2 fusion proteins used in the MS2-tethering assay are shown. (C) Quantitation of luciferase activity in 293 cells transfected with plasmids encoding the indicated MS2 fusion proteins. (D) Western for TAP in TAP knockdown cells. Tubulin was used as loading control. (E) MS2/RRE tethering assay in TAP knockdown cells. (F) MS2/RRE-tethering assay in Leptomycin B-treated cells. MS2 assay results represent the average values obtained from nine independent transfections, and error bars show the standard deviations.