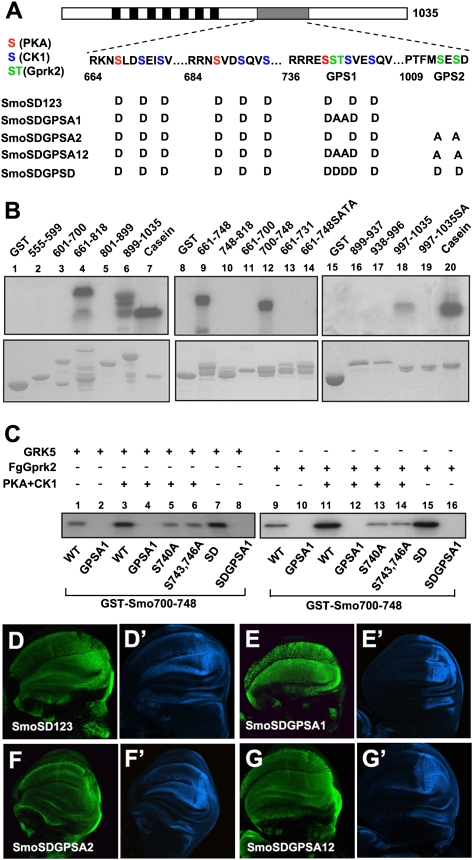
Figure 3.
GRK phosphorylates multiple sites in Smo C-tail. (A) A schematic drawing of Smo with the sequence surrounding the PKA/CK1 sites and GRK sites (GPS1 and GPS2) shown below. PKA, CK1, and GRK sites are indicated by red, blue, and green residues, respectively. The transmembrane domains are indicated by the black boxes, and the SAID is indicated by the gray bar. Amino acid substitutions for SmoSD123 and its derivatives are listed. (B) In vitro kinase assay using a recombinant GRK5 and GST fusion proteins carrying indicated fragments from the Smo C-tail. (Lanes 12,18) Two minimal fragments, amino acids 700–748 and amino acids 997–1035, were phosphorylated by GRK5. (Lanes 14,19) Mutating the S741/T742 or S1013/S1015 abolished phosphorylation of the corresponding fragments. (C) In vitro kinase assay using recombinant GRK5 (shown in lanes 1–8) or immunoprecipitated Fg-Gprk2 with GST-Smo700–748 bearing the wild-type sequence or indicated point mutations. PKA/CK1 pretreatment was carried out in the presence of cold ATP. (D–G′) Wing discs expressing CFP-tagged SmoSD123 (D,D′), SmoSDGPSA1 (E,E′), SmoSDGPSA2 (F,F′), or SmoSDGPSA12 (G,G′) were immunostained to show the expression of CFP (green) and en (blue). SmoSD123 and SmoSDGPSA2 but not SmoSDGPSA1 or SmoSDGPSA12 induced ectopic en expression.