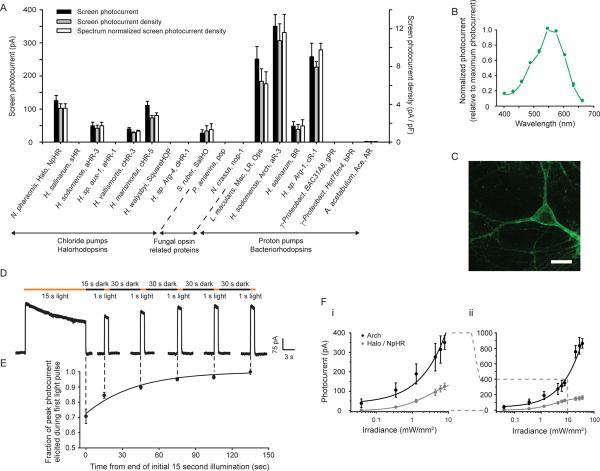
Figure 1.
Optical neural silencing via light-driven proton pumping, revealed by a cross-kingdom functional molecular screen. (A) Screen data showing outward photocurrents (left ordinate, black bars), photocurrent densities (right ordinate, gray bars), and action spectrum-normalized photocurrent densities (right ordinate, white bars), measured via whole-cell patch clamp of cultured neurons under screening illumination conditions (575±25 nm, 7.8 mW/mm2 for all but Mac/LR/Ops, gPR, bPR, and Ace/AR, which were 535±25 nm, 9.4 mW/mm2; see Supplementary Table 1 for details on the molecules screened; N = 4–16 neurons for each bar). All data in this and other figures are mean ± standard error (SE) unless otherwise indicated. (B) Action spectrum of Arch measured in cultured neurons by scanning illumination light wavelength through the visible spectrum (N = 7 neurons). (C) Confocal fluorescence image of a lentivirally-infected cultured neuron expressing Arch-GFP (scale bar, 20 μm). (D) Raw current trace of a neuron lentivirally-infected with Arch, illuminated by a 15 s light pulse (575 ± 25 nm, irradiance 7.8 mW/mm2), followed by 1 s test pulses delivered starting 15, 45, 75, 105, and 135 seconds after the end of the 15 s light pulse. (E) Population data of averaged Arch photocurrents (N = 11 neurons) sampled at the times indicated by the vertical dotted lines that extend into Fig. 1D. (F) Photocurrents of Arch vs. Halo measured as a function of 575 ± 25 nm light irradiance (or effective light irradiance; see Methods for details), in patch-clamped cultured neurons (N = 4 – 16 neurons for each point), for low (i) and high (ii) light powers. The line is a single Hill fit to the data.