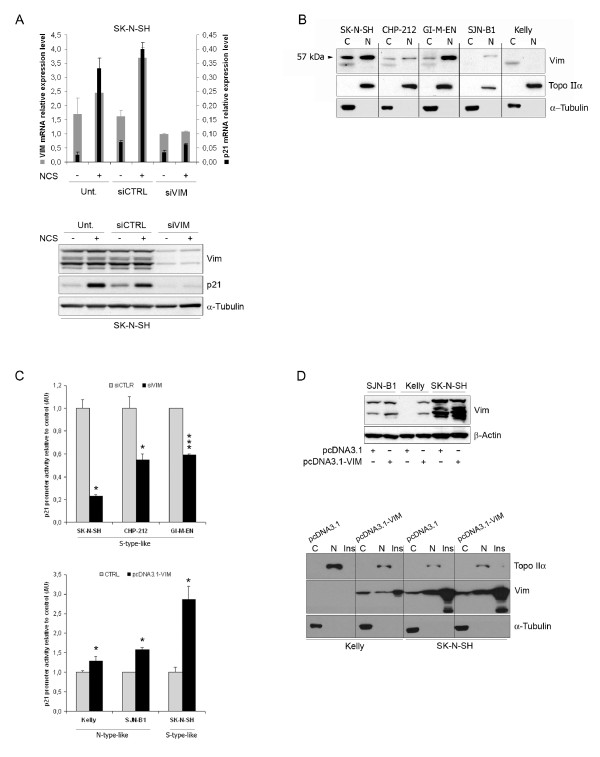
Figure 2.
Vimentin participates in p21 transcriptional regulation. A. Vimentin or p21 gene expression was monitored by Q-PCR analysis (upper panel), as described in Figure 1A. Vimentin or p21 protein levels in total cellular extracts were assessed by immunoblotting, α-Tubulin being used as loading control (lower panel). Cells were left untransfected (Unt.) or were transfected with the siRNAs targeting vimentin (siVIM) or control siRNA (siCTRL). Cells were either untreated (-) or NCS-treated (+). This figure is representative of 3 independent experiments. NCS: neocarzinostatin. B. Subcellular localization of soluble vimentin assessed by differential fractionation (C, Cytoplasmic; N, nuclear) followed by Western blot analysis in SK-N-SH, CHP-212, GI-MEN, SJN-B1 and Kelly cells lines. Topoisomerase IIα and α-Tubulin are used as controls for the nuclear and cytoplasmic soluble fractions, respectively. C. Analysis of p21 promoter activity using luciferase assay in indicated S- or N-type-like NB cell lines, either downregulated (siVIM) or not (siCTRL) for vimentin expression (upper panel), or overexpressing (pcDNA3.1-VIM) or not (CTRL: pcDNA3.1) vimentin (lower panel). Comparisons were assessed with the Mann-Whitney statistical test (* and *** stand for p < 0.05 and p < 0.005 respectively). The graph is representative of 3 independent experiments. D. Upper panel: Western Blot analysis of vimentin expression in indicated cells transiently transfected with pcDNA3.1-VIM or the empty vector (pcDNA3.1). β-actin is used as loading control. Lower panel: Vimentin cellular distribution (C, Cytoplasmic soluble; N, nuclear soluble; Ins., Insoluble cytoskeletal/matrix-associated fractions) in vimentin overexpressing cells, assessed by differential cellular fractionation followed by Western Blot analysis. Topoisomerase IIα and α-Tubulin are used as controls for the nuclear and cytoplasmic soluble fractions, respectively.