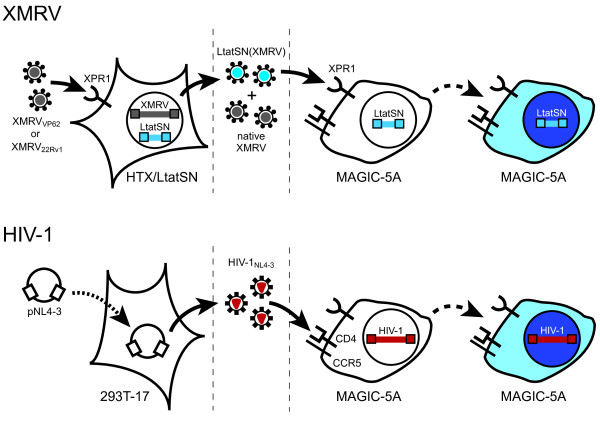
Figure 1.
Drug susceptibility assays for XMRV and HIV-1. For XMRV, HTX/LtatSN cells were infected (solid arrows) with XMRV22Rv1 or XMRVVP62, resulting in the release of native XMRV (gray virions) as well as XMRV-pseudotyped virions that contain LtatSN RNA (LtatSN(XMRV); blue virions). Infection of MAGIC-5A cells with XMRV+LtatSN results in transfer of the HIV-1 tat marker gene, thereby inducing β-gal expression through Tat-dependent transactivation of an upstream HIV-1 LTR promoter. β-gal+ (blue) cells are detected by staining the MAGIC-5A monolayers with X-gal (dashed arrows). Entry of XMRV into HTX/LtatSN and MAGIC-5A cells is mediated by the endogenously-expressed xenotropic and polytropic retrovirus receptor 1 (XPR1). For HIV-1, virus stocks were produced by transient transfection (dotted arrow) of 293T/17 cells with pNL4-3. As with XMRV+LtatSN, infection of MAGIC-5A cells with HIV-1NL4-3 (red virions) results in Tat expression and β-gal+ focus formation. MAGIC-5A cells were previously engineered to express the CD4 receptor and CCR5 coreceptor for HIV-1 entry; these cells also express the endogenous CXCR4 coreceptor [26]. Dashed vertical lines indicate the stages at which protease inhibitors (left) and reverse transcriptase or integrase inhibitors (right) were added to the culture supernatants.