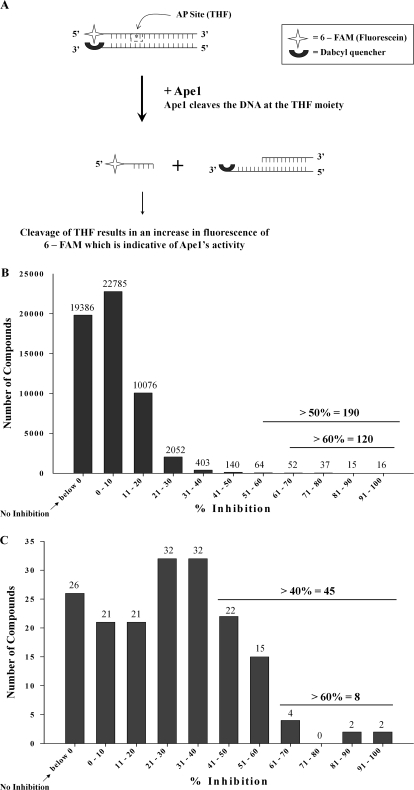
Fig. 1.
HTS assay to identify inhibitors of Ape1. A, principle of the HTS Assay. This figure represents the principle of the modified fluorescent HTS assay used for our screening purposes. The fluorescence of 6-FAM is diminished by Q because of their proximity to each other. On addition of Ape1, it cleaves the THF residue releasing the short 6-FAM-labeled fragment that results in a proportionate increase in fluorescence. This increase in fluorescence can be considered to be an indirect measure of cleavage activity of Ape1. B, results of the initial screen of the 60,000-compound library. After the screen of the entire library, we identified 190 compounds that inhibited the activity of Ape1 by 50% or more. C, results of a secondary screen of all the hits from the initial screen showing ≥50% inhibition of the activity of Ape1. Of the 190 compounds identified, 174 were retested in this same assay to weed out false positives, and 41 compounds with ≥40% inhibition of the DNA repair activity of Ape1 were validated. For both B and C, the graphs are representations of the numbers of compounds plotted with their corresponding percentage of inhibition of the activity of Ape1.